

Literature Review - what is a Literature Review, why it is important and how it is done
What are literature reviews, goals of literature reviews, types of literature reviews, about this guide/licence.
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Literature Reviews and Sources
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
- Useful Resources
Help is Just a Click Away
Search our FAQ Knowledge base, ask a question, chat, send comments...
Go to LibAnswers
What is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries. " - Quote from Taylor, D. (n.d) "The literature review: A few tips on conducting it"
Source NC State University Libraries. This video is published under a Creative Commons 3.0 BY-NC-SA US license.
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review?
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
- Baumeister, R.F. & Leary, M.R. (1997). "Writing narrative literature reviews," Review of General Psychology , 1(3), 311-320.
When do you need to write a Literature Review?
- When writing a prospectus or a thesis/dissertation
- When writing a research paper
- When writing a grant proposal
In all these cases you need to dedicate a chapter in these works to showcase what have been written about your research topic and to point out how your own research will shed a new light into these body of scholarship.
Literature reviews are also written as standalone articles as a way to survey a particular research topic in-depth. This type of literature reviews look at a topic from a historical perspective to see how the understanding of the topic have change through time.
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
- Narrative Review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Book review essays/ Historiographical review essays : This is a type of review that focus on a small set of research books on a particular topic " to locate these books within current scholarship, critical methodologies, and approaches" in the field. - LARR
- Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L.K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . San Diego, CA: Plural Publishing.
- Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M.C. & Ilardi, S.S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Malden, MA: Blackwell Pub.
- Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). "Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts," Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53(3), 311-318.
Guide adapted from "Literature Review" , a guide developed by Marisol Ramos used under CC BY 4.0 /modified from original.
- Next: Strategies to Find Sources >>
- Last Updated: Jul 3, 2024 10:56 AM
- URL: https://lit.libguides.com/Literature-Review
The Library, Technological University of the Shannon: Midwest
- +91 9884350006
- +1-972-502-9262
- [email protected]

Why is it important to do a literature review in research?
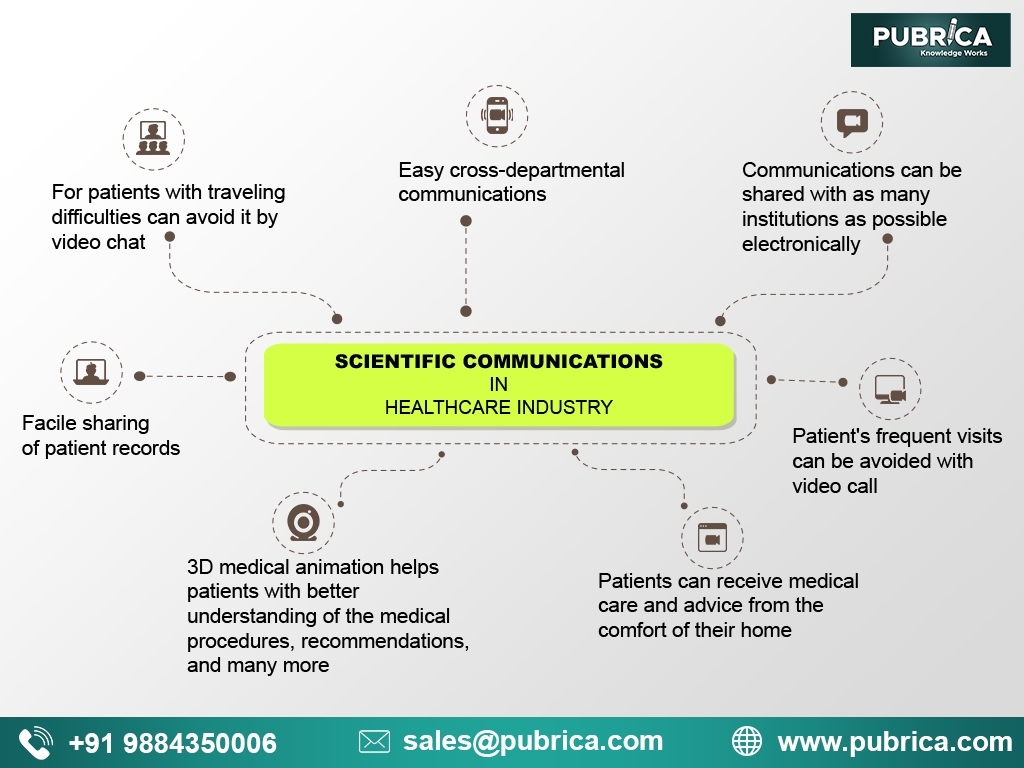
The importance of scientific communication in the healthcare industry
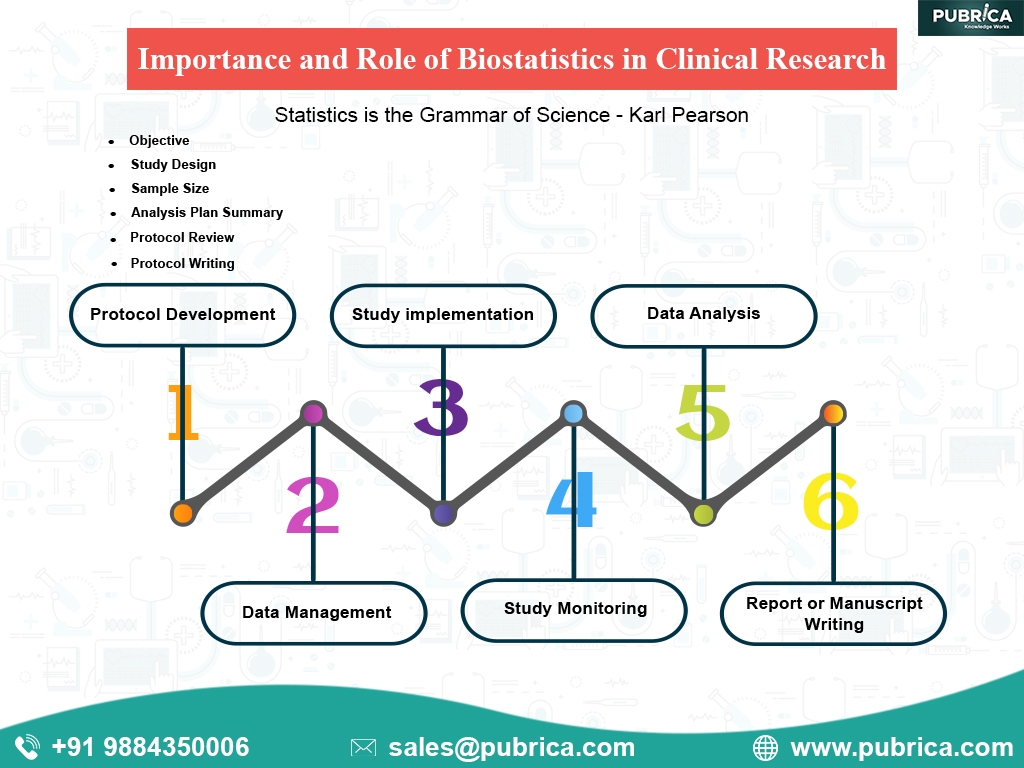
The Importance and Role of Biostatistics in Clinical Research
“A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research”. Boote and Baile 2005
Authors of manuscripts treat writing a literature review as a routine work or a mere formality. But a seasoned one knows the purpose and importance of a well-written literature review. Since it is one of the basic needs for researches at any level, they have to be done vigilantly. Only then the reader will know that the basics of research have not been neglected.
The aim of any literature review is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of existing knowledge in a particular field without adding any new contributions. Being built on existing knowledge they help the researcher to even turn the wheels of the topic of research. It is possible only with profound knowledge of what is wrong in the existing findings in detail to overpower them. For other researches, the literature review gives the direction to be headed for its success.
The common perception of literature review and reality:
As per the common belief, literature reviews are only a summary of the sources related to the research. And many authors of scientific manuscripts believe that they are only surveys of what are the researches are done on the chosen topic. But on the contrary, it uses published information from pertinent and relevant sources like
- Scholarly books
- Scientific papers
- Latest studies in the field
- Established school of thoughts
- Relevant articles from renowned scientific journals
and many more for a field of study or theory or a particular problem to do the following:
- Summarize into a brief account of all information
- Synthesize the information by restructuring and reorganizing
- Critical evaluation of a concept or a school of thought or ideas
- Familiarize the authors to the extent of knowledge in the particular field
- Encapsulate
- Compare & contrast
By doing the above on the relevant information, it provides the reader of the scientific manuscript with the following for a better understanding of it:
- It establishes the authors’ in-depth understanding and knowledge of their field subject
- It gives the background of the research
- Portrays the scientific manuscript plan of examining the research result
- Illuminates on how the knowledge has changed within the field
- Highlights what has already been done in a particular field
- Information of the generally accepted facts, emerging and current state of the topic of research
- Identifies the research gap that is still unexplored or under-researched fields
- Demonstrates how the research fits within a larger field of study
- Provides an overview of the sources explored during the research of a particular topic
Importance of literature review in research:
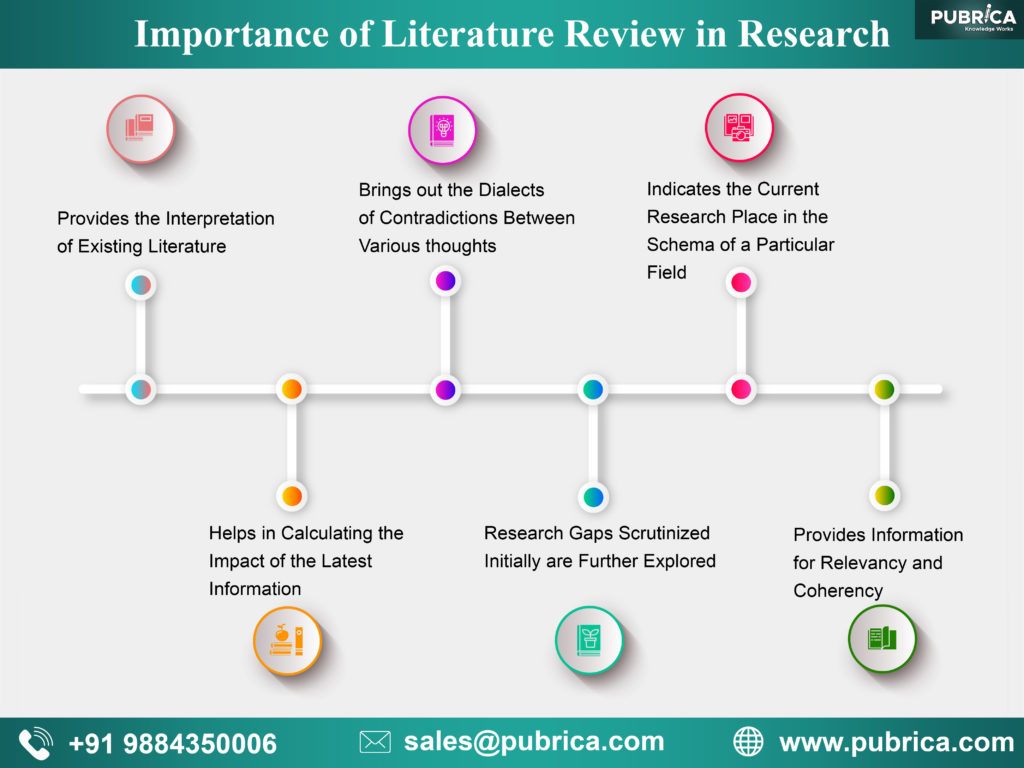
The importance of literature review in scientific manuscripts can be condensed into an analytical feature to enable the multifold reach of its significance. It adds value to the legitimacy of the research in many ways:
- Provides the interpretation of existing literature in light of updated developments in the field to help in establishing the consistency in knowledge and relevancy of existing materials
- It helps in calculating the impact of the latest information in the field by mapping their progress of knowledge.
- It brings out the dialects of contradictions between various thoughts within the field to establish facts
- The research gaps scrutinized initially are further explored to establish the latest facts of theories to add value to the field
- Indicates the current research place in the schema of a particular field
- Provides information for relevancy and coherency to check the research
- Apart from elucidating the continuance of knowledge, it also points out areas that require further investigation and thus aid as a starting point of any future research
- Justifies the research and sets up the research question
- Sets up a theoretical framework comprising the concepts and theories of the research upon which its success can be judged
- Helps to adopt a more appropriate methodology for the research by examining the strengths and weaknesses of existing research in the same field
- Increases the significance of the results by comparing it with the existing literature
- Provides a point of reference by writing the findings in the scientific manuscript
- Helps to get the due credit from the audience for having done the fact-finding and fact-checking mission in the scientific manuscripts
- The more the reference of relevant sources of it could increase more of its trustworthiness with the readers
- Helps to prevent plagiarism by tailoring and uniquely tweaking the scientific manuscript not to repeat other’s original idea
- By preventing plagiarism , it saves the scientific manuscript from rejection and thus also saves a lot of time and money
- Helps to evaluate, condense and synthesize gist in the author’s own words to sharpen the research focus
- Helps to compare and contrast to show the originality and uniqueness of the research than that of the existing other researches
- Rationalizes the need for conducting the particular research in a specified field
- Helps to collect data accurately for allowing any new methodology of research than the existing ones
- Enables the readers of the manuscript to answer the following questions of its readers for its better chances for publication
- What do the researchers know?
- What do they not know?
- Is the scientific manuscript reliable and trustworthy?
- What are the knowledge gaps of the researcher?
22. It helps the readers to identify the following for further reading of the scientific manuscript:
- What has been already established, discredited and accepted in the particular field of research
- Areas of controversy and conflicts among different schools of thought
- Unsolved problems and issues in the connected field of research
- The emerging trends and approaches
- How the research extends, builds upon and leaves behind from the previous research
A profound literature review with many relevant sources of reference will enhance the chances of the scientific manuscript publication in renowned and reputed scientific journals .
References:
http://www.math.montana.edu/jobo/phdprep/phd6.pdf
journal Publishing services | Scientific Editing Services | Medical Writing Services | scientific research writing service | Scientific communication services
Related Topics:
Meta Analysis
Scientific Research Paper Writing
Medical Research Paper Writing
Scientific Communication in healthcare

The Guide to Literature Reviews

- What is a Literature Review?
- Introduction
What is the purpose of a literature review?
The importance of literature reviews: industry examples, important reminders.
- Guidelines for Writing a Literature Review
- How to Organize a Literature Review?
- Software for Literature Reviews
- Using Artificial Intelligence for Literature Reviews
- How to Conduct a Literature Review?
- Common Mistakes and Pitfalls in a Literature Review
- Methods for Literature Reviews
- What is a Systematic Literature Review?
- What is a Narrative Literature Review?
- What is a Descriptive Literature Review?
- What is a Scoping Literature Review?
- What is a Realist Literature Review?
- What is a Critical Literature Review?
- Meta Analysis vs. Literature Review
- What is an Umbrella Literature Review?
- Differences Between Annotated Bibliographies and Literature Reviews
- Literature Review vs. Theoretical Framework
- How to Write a Literature Review?
- How to Structure a Literature Review?
- How to Make a Cover Page for a Literature Review?
- How to Write an Abstract for a Literature Review?
- How to Write a Literature Review Introduction?
- How to Write the Body of a Literature Review?
- How to Write a Literature Review Conclusion?
- How to Make a Literature Review Bibliography?
- How to Format a Literature Review?
- How Long Should a Literature Review Be?
- Examples of Literature Reviews
- How to Present a Literature Review?
- How to Publish a Literature Review?
The Purpose of Literature Reviews
A literature review has various purposes, one of the most important is the identification of knowledge gaps in a specific topic. It also helps to understand the current state of knowledge of a research topic and guides the researcher into unexplored terrain. A good literature review helps answer questions such as how will this research contribute to the scientific community and why is this something new and interesting worth further investigation. For example, qualitative researchers may find that some topics have been covered quantitatively but not qualitatively.

A useful analogy when conducting a literature review is to think of a forest, where a researcher must describe the forest and not every tree inside it. In a literature review, researchers are essentially telling a story about the research problem they are addressing, why this research problem is important, and how they contribute new understanding of this problem. They develop their arguments in a research project based on the existing literature, constructing a narrative supported by the findings of their study. This first research step involves strict organization and a strong critical analysis of the previous literature. It also serves as a foundation for selecting and assessing the most effective methodologies and methods. For example, whether in-depth interviews or focus groups have worked better for similar research or if a grounded theory methodology is better than a narrative methodology for the study.
Researchers can write an entire paper that is based only on a comprehensive literature review, summarizing research around a topic and providing guidelines for further research. More commonly, however, the literature review is presented at the beginning of an empirical study to lay the foundation on which the researcher's subsequent data collection and analysis is based. Researchers conduct literature reviews to avoid reinventing the wheel and ensure they are looking at the most updated existing knowledge on their topic of research. Reviewing relevant articles provides a solid foundation and context for the research, helping to establish where the new research fits within the existing body of work.
A literature review also helps build a theoretical framework , which guides the study and helps interpret the findings. By engaging with existing conclusions, theories, and models, a researcher ensures the study is connected to a broader scholarly conversation and the research topic is approached with a well-informed perspective. A literature review is the primary means through which researchers construct their arguments to justify the need for their research. Rather than "only" summarizing previous research, the literature review should clearly explain the author's reasoning for why studying this topic or research problem is important and contributes novel and interesting knowledge.
Another critical purpose of a literature review is to contextualize the new research within the existing body of knowledge. The researcher can demonstrate relevance by comparing their research objectives with those of previous studies. This comparison helps them understand how their new study addresses gaps or adds new insights. For example, a qualitative study on workplace motivation might build upon existing research, adding depth to our understanding of employee experiences and the nuances of motivational factors.

Finally, a researcher doing a thorough literature review of previous research can provide a roadmap for future studies. By conducting the review , the researcher will discover the gaps of knowledge that can be filled by their research as well as discover roadmaps of knowledge that other researchers can uptake. For example, in the field of education, a literature review might reveal a lack of qualitative studies on the different, numerous experiences of students with a disability, prompting further research in this area overall. The literature review solidifies the research focus and enhances the quality and relevance of the study.
When it comes to conducting a literature review for a qualitative study, it is important to recognize that the literature review is a highly iterative process, often occurring before, during, and after data analysis. While some highly inductive qualitative studies may delay engaging with a literature review until after their data has been analyzed, no researcher begins their study with a purely "blank mind" and has no familiarity with any relevant literature. For example, researchers read relevant literature to understand what is currently known about their research problem and what questions remain unanswered. In addition, reading key studies can provide researchers with "sensitizing concepts", or ideas about key concepts worth pursuing further in one's research and data collection (Blumer, 1969). After data has been analyzed, it is also crucial to revisit the literature in light of one's findings and highlight how these findings contribute to broader scholarly conversation. In other words, regardless of when qualitative researchers engage with the literature review, all researchers need to engage in literature reviews to understand current conversations around their topic and discern how they can contribute something new and interesting to this ongoing conversation.
Quality literature reviews start with ATLAS.ti
From the research objective to the conclusion, ATLAS.ti is there for you at every step. See how with a free trial.
Literature reviews play an essential role across various industries. From general overviews to building a theoretical foundation using existing theories, literature reviews focus on extant literature and shine a light on areas that need further investigation. The following examples illustrate the significance of literature reviews in healthcare, business and marketing, environmental studies, and education.
In healthcare research, a sophisticated literature review may reveal gaps in understanding patient experiences with chronic illnesses or other aspects such as experiences when dealing with medical professionals. Researchers can develop more patient-centred care practices by conducting a systematic literature review and critical evaluation of empirical evidence. Another example is how researchers can have a baseline of knowledge of the emotional impact of diabetes management in young adults if they conduct narrative literature reviews . This helps refine their research questions or research methods to focus specifically on an age group and avoid the redundancy of studying well-covered topics such as general diabetes management. These are just some examples of literature review objectives that a healthcare researcher may have.
Business and marketing
In business and marketing research, the purpose of a literature review is immensely valuable. Business and marketing literature may show extensive quantitative data on consumer behaviour trends but that lack qualitative insights into consumer decision-making processes. Qualitative research , such as in-depth interviews with consumers, can uncover the underlying motivations and attitudes that drive purchasing decisions, thereby highlighting the value of a literature review for advancing marketing strategies. For example, when investigating consumer behaviour toward eco-friendly products, a literature review can reveal gaps such as a limited understanding of purchasing motivations among millennials. This allows researchers to focus their own research on this particular topic, refining their research questions to address specific factors influencing millennials' purchasing decisions. After doing a comprehensive literature review, researchers can determine additional focus areas and direct research efforts to explore emerging trends.
Environmental studies
In environmental qualitative research , literature reviews are critical. For example, when exploring community perceptions of renewable energy projects, reviewing relevant literature can identify a limited understanding of local cultural influences on these perceptions. This allows researchers to refine their research questions to delve into cultural factors affecting community acceptance. Literature reviews also help identify theoretical frameworks , such as social acceptance theory, to guide analysis and interpretation . This ensures that the research paper is original and adds valuable insights into renewable energy adoption. Understanding the current research landscape helps researchers pinpoint additional focus areas, such as the role of local leadership in shaping perceptions, and direct research efforts accordingly.
Qualitative education research is essential when examining the impact of teaching methods on student experience. The literature review can identify gaps, such as a lack of understanding about how specific pedagogical approaches influence diverse student populations. This helps the researcher address specific factors that influence student engagement. Another example is when literature reviews highlight the need for more qualitative studies on the experiences of minority students in higher education. This enables them to understand student challenges and develop interventions to support their success.

A literature review is indispensable across various industries because it provides a comprehensive understanding of existing research, identifies gaps, and lays the groundwork for new studies. It ensures that research efforts are not duplicated and promotes the advancement of knowledge. It also offers a well-informed basis for interpreting new findings. Researchers can contribute meaningful insights and innovations to their fields by critically evaluating and synthesizing existing literature. Whether in healthcare, business, environmental studies, education, or any other area, literature reviews drive progress and ensure that research remains relevant and impactful.
Literature reviews foster academic dialogue by highlighting underexplored areas and suggesting directions for future research. This ongoing exchange of ideas and findings enhances the collective understanding within each industry, promoting collaboration and continuous improvement. The different approaches of literature reviews are different approaches to ensure a thorough examination of the topic, providing a solid foundation for empirical studies and theoretical advancements.
Ultimately, literature reviews are more than just a preliminary step in the research process; they are pivotal in shaping the trajectory of scholarly inquiry and practical applications. Literature reviews help bridge the gap between theory and practice, by grounding new research in a well-established context. The literature review validates new research and strengthens its relevance and impact across diverse fields.
- Blumer. H. (1969). Symbolic interactionism. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.

Develop powerful literature reviews with ATLAS.ti
Use our intuitive data analysis platform to make the most of your literature review. Get started with a free trial.
The Importance of Literature Review in Academic Writing

The literature review holds paramount importance in academic writing for several reasons. Firstly, it serves as a comprehensive survey of existing research, establishing a solid foundation for the author’s work. It helps identify gaps, trends, and debates in the chosen field, guiding researchers toward relevant and valuable contributions. Additionally, a well-crafted literature review demonstrates the author’s understanding of the subject, showcases critical thinking skills, and enhances the credibility of the academic work by contextualizing it within the broader scholarly conversation. Overall, the literature review is an indispensable component that enriches the depth and quality of academic writing.
What is the role of a literature review in academic writing
The literature review plays a crucial role in academic writing by serving several important functions;
- Establishing Context: A literature review provides the context for the research by summarizing and synthesizing existing knowledge on the chosen topic. It helps readers understand the background and the current state of the subject matter.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: Through a literature review, researchers can identify gaps, controversies, or areas where more research is needed. This helps in justifying the significance of the new study and contributing to the existing body of knowledge.
- Formulating Research Questions or Hypotheses: By reviewing existing literature, researchers can derive relevant research questions or hypotheses. This ensures that the study is informed by and contributes to the broader academic discourse.
- Building a Theoretical Framework: A literature review helps in building the theoretical framework for a study by examining and summarizing relevant theories and concepts from previous research. It provides a conceptual foundation for the current research.
- Selecting Methodology: Understanding how previous studies were conducted helps researchers in selecting an appropriate methodology for their own research. It also assists in avoiding potential pitfalls or methodological errors.
- Avoiding Duplication: Researchers can identify what has already been done, preventing duplication of efforts. This helps in ensuring that the new study adds value and contributes to the existing knowledge.
- Critically Evaluating Sources: A literature review involves a critical analysis of the quality and reliability of the sources. This ensures that the information used in the study is credible and relevant.
- Synthesizing Information: A literature review involves synthesizing information from various sources to present a cohesive and comprehensive understanding of the topic. It helps in drawing connections and patterns in the existing research.
- Providing a Historical Perspective: It offers a historical perspective on the development of ideas and concepts within a specific field, allowing readers to trace the evolution of thought over time.
- Supporting or Challenging Arguments: The literature review supports the author’s arguments by presenting evidence from existing research. It may also highlight conflicting findings or alternative perspectives that contribute to a balanced discussion.
In summary, the literature review is a critical component of academic writing, serving as a foundation for the research, guiding methodology, and contributing to the scholarly conversation within a particular field.
How does a literature review contribute to the overall quality of a research paper
A literature review contributes significantly to the overall quality of a research paper in several ways:
- Establishing Credibility: By reviewing relevant and reputable sources, a literature review helps establish the credibility of the research. It shows that the author is well-informed about existing scholarship on the topic.
- Identifying Research Gaps: The literature review identifies gaps, controversies, or unanswered questions in the current body of knowledge. This not only justifies the need for the new study but also highlights its potential contribution to the field.
- Providing Context and Background: A literature review provides context by summarizing and synthesizing existing research. It helps readers understand the historical development, key concepts, and current state of the research topic.
- Guiding Research Questions or Hypotheses: The literature review informs the formulation of research questions or hypotheses by revealing what is already known and what remains unknown in the field. This ensures that the study is focused and relevant.
- Building a Theoretical Framework: It contributes to building a theoretical framework by examining and summarizing relevant theories and concepts. This theoretical foundation helps structure the research and guide the analysis.
- Selecting Appropriate Methodology: Knowledge of how previous studies were conducted informs the choice of methodology for the new research. This ensures that the research design is well-suited to address the specific objectives of the study.
- Avoiding Duplication: The literature review helps prevent duplication of efforts by identifying what has already been studied. This ensures that the new research contributes something novel to the existing body of knowledge.
- Providing a Critical Analysis: A literature review involves critically evaluating the quality, reliability, and relevance of sources. This ensures that only credible and pertinent information is included in the research paper.
- Synthesizing Information: By synthesizing information from diverse sources, a literature review presents a comprehensive and cohesive understanding of the research topic. It helps in drawing connections and identifying patterns in the existing literature.
- Supporting Arguments: The literature review supports the author’s arguments and hypotheses by providing evidence from previous studies. It demonstrates how the current research fits into the broader scholarly conversation.
In essence, a well-executed literature review enhances the overall quality of a research paper by providing a solid foundation, guiding the research process, and ensuring that the study contributes meaningfully to the academic discourse in its respective field.
What are the key objectives of conducting a literature review in academic research
The key objectives of conducting a literature review in academic research include;
- Identifying Existing Knowledge: To review and summarize the current state of knowledge on a particular topic or research question, understanding what is already known.
- Establishing Context: To provide the necessary background and context for the research, helping readers understand the significance of the study.
- Identifying Gaps and Research Questions: To identify gaps, controversies, or areas where further research is needed, which helps in formulating specific research questions or hypotheses.
- Building a Theoretical Framework: To review and synthesize relevant theories and concepts that will form the theoretical foundation of the research.
- Guiding Methodology: To inform the selection of appropriate research methodologies and methods based on the strengths and weaknesses of previous studies.
- Avoiding Duplication: To ensure that the research contributes something new to the existing body of knowledge, preventing unnecessary duplication of previous studies.
- Critical Evaluation: To critically evaluate the quality, reliability, and validity of existing literature, ensuring that only credible sources are used to support the research.
- Synthesizing Information: To synthesize information from diverse sources, presenting a cohesive and comprehensive understanding of the topic.
- Identifying Key Concepts and Variables: To identify and define key concepts, variables, and terms relevant to the research study.
- Understanding Methodological Approaches: To understand how previous studies were conducted, helping researchers learn from successes and pitfalls in methodology.
- Recognizing Trends and Patterns: To identify trends, patterns, and recurring themes in the literature, providing insights into the broader context of the research.
- Contextualizing Findings: To place the research findings in the context of existing knowledge, allowing for a more nuanced interpretation of results.
- Informing Literature Selection: To guide the selection of literature relevant to the research topic, ensuring that the review is focused and comprehensive.
- Supporting or Challenging Arguments: To provide evidence and support for the arguments or hypotheses presented in the research, or to highlight conflicting findings in the literature.
- Contributing to Theoretical Debates: To actively contribute to theoretical debates and discussions within the academic field.
- Enhancing the Rigor of Research: To enhance the overall rigor and validity of the research by basing it on a solid foundation of existing knowledge.
The objectives of a literature review in academic research are multi-faceted, ranging from understanding existing knowledge to guiding the research process and ensuring the credibility and significance of the study.
How does a literature review help establish the research gap in a particular field
A literature review plays a crucial role in identifying and establishing the research gap in a particular field through the following mechanisms;
- Summarizing Existing Knowledge: The literature review provides a comprehensive summary of existing research on a given topic, allowing researchers to understand the current state of knowledge in the field.
- Identifying Patterns and Trends: By reviewing multiple studies, a literature review helps researchers identify patterns, trends, and common themes in the existing literature. This analysis highlights areas where research has been concentrated and areas where it may be lacking.
- Highlighting Consensus and Controversies: The literature review reveals areas where there is a consensus among researchers and areas where there are conflicting findings or ongoing debates. This can point to gaps in understanding that require further investigation.
- Pointing to Unanswered Questions: As researchers analyze the literature, they may come across questions that have not been adequately addressed or answered by existing studies. These unanswered questions signify potential research gaps.
- Examining Methodological Limitations: A thorough literature review involves evaluating the methodologies employed in previous studies. Identifying limitations or gaps in methodology can suggest areas where further research is needed to address these shortcomings.
- Assessing Currency of Information: If there is a lack of recent studies on a specific aspect of a topic, it may indicate that there is a gap in recent research that needs attention.
- Considering Emerging Trends: The literature review allows researchers to identify emerging trends or new developments in the field. These trends may open up avenues for novel research directions.
- Evaluating Geographical or Cultural Gaps: Geographical or cultural gaps in the literature can also indicate areas where further research is needed to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the topic.
- Analyzing Changes Over Time: A temporal analysis of the literature can reveal how research on a particular topic has evolved. Recognizing changes and shifts in focus over time may uncover gaps in understanding that need addressing.
- Seeking Gaps in Application: Researchers can identify gaps in the application of theoretical frameworks or interventions within practical settings. This may suggest opportunities for applied research.
By systematically examining the existing literature and critically evaluating its content, methodologies, and findings, researchers can pinpoint areas where knowledge is incomplete or where further investigation is necessary. Identifying these gaps helps shape the rationale for the new study and positions it within the broader context of the existing body of knowledge.
In what ways does a literature review assist in framing research questions and hypotheses
A literature review assists in framing research questions and hypotheses in several ways;
- Identification of Existing Knowledge: A literature review provides an overview of existing knowledge on a particular topic, helping researchers understand what has already been studied and established in the field.
- Identification of Gaps: By analyzing the existing literature, researchers can identify gaps, limitations, or unanswered questions. These gaps serve as a basis for formulating research questions, as they highlight areas where new knowledge is needed.
- Understanding Theoretical Foundations: The literature review helps researchers understand the theoretical frameworks and concepts that have been used in previous studies. This understanding guides the formulation of research questions that align with established theories or challenge existing paradigms.
- Inspiration from Previous Research: Reviewing the literature provides researchers with insights and inspiration from previous studies. It helps them identify interesting phenomena, patterns, or trends that can lead to the formulation of relevant and meaningful research questions.
- Identification of Variables: Researchers can identify key variables, factors, or elements that have been studied in the literature. This identification informs the formulation of hypotheses and guides the operationalization of variables in the research design.
- Clarity in Focus: A literature review helps researchers narrow down the scope of their study by clarifying the focus and defining the specific aspects of the topic that need further investigation. This clarity contributes to the formulation of precise and focused research questions.
- Understanding Methodologies: By examining the methodologies used in previous studies, researchers gain insights into various research approaches. This understanding guides the selection of an appropriate research methodology for their own study, influencing the formulation of research questions.
- Building on Previous Findings: Researchers may build on or extend previous findings identified in the literature. Formulating research questions in the context of existing research allows for the advancement of knowledge and contributes to the ongoing scholarly conversation.
- Alignment with Research Goals: The literature review helps researchers align their research questions with the overarching goals and objectives of the study. This ensures that the research questions are relevant and contribute meaningfully to the field.
- Contextualizing Hypotheses: Based on the insights gained from the literature review, researchers can formulate hypotheses that are grounded in existing theories or empirical evidence. This contextualization strengthens the rationale for the hypotheses.
A well-conducted literature review informs and guides the process of formulating research questions and hypotheses by providing a foundation of knowledge, highlighting gaps, and offering insights from previous studies. This ensures that the research questions are relevant, theoretically grounded, and contribute to the advancement of the field.
Can a well-conducted literature review enhance the credibility of academic research
Yes! A well-conducted literature review is essential for enhancing the credibility of academic research in several ways;
1. Demonstrates Expertise: A comprehensive review shows you have a deep understanding of the existing knowledge and relevant theory in your field. This establishes you as an authority and positions your research within the broader context.
2. Justifies Significance: By reviewing past studies, you can clarify the gaps in research and highlight why your project addresses a crucial, unanswered question. This strengthens the purpose and originality of your work.
3. Supports Methodological Choices: You can use past research to justify your chosen methods, data collection, and analysis strategies. This demonstrates rigor and helps readers understand how your work builds upon previous findings.
4. Identifies Limitations and Strengths: Recognizing strengths and limitations of earlier studies allows you to position your research strategically. You can address limitations of past work or build upon their strengths, demonstrating a critical and informed approach.
5. Shows Engagement with the Field: Engaging with other scholars' work showcases your awareness of ongoing debates and conversations in your field. This demonstrates you are actively contributing to the advancement of knowledge.
Beyond Credibility:
A strong literature review goes beyond just building trust. It can also:
- Spark new research ideas: Examining diverse perspectives can trigger innovative ways to approach your research question.
- Identify potential challenges: Awareness of previous difficulties can help you anticipate and address similar issues in your study.
- Strengthen your arguments: Referencing relevant findings bolsters your conclusions and persuades readers of their validity.
- Thoroughness matters: Aim for a comprehensive review, including both supportive and opposing viewpoints.
- Critical analysis is key: Don’t just summarize; evaluate, compare, and contrast different studies to demonstrate your critical thinking skills.
- Clarity is crucial: Organize your review logically and present it in a clear, concise, and easy-to-follow manner.
By investing time and effort in conducting a well-structured and insightful literature review, you’ll lay a solid foundation for your research and significantly enhance its credibility and potential impact.
How does the literature review process aid in identifying key theories and concepts relevant to the research topic
The literature review process plays a crucial role in identifying key theories and concepts relevant to your research topic in several ways;
1. Exposure to Existing Knowledge: As you dive into relevant scholarly articles, books, and other sources, you’ll be exposed to the prevailing theories and concepts surrounding your topic. This initial immersion provides a broad understanding of the landscape and potential key players.
2. Identifying Recurring Themes and Ideas: As you analyze and synthesize the collected information, you’ll start noticing recurring themes, terminologies, and arguments. These recurrent elements likely represent the key theories and concepts shaping the field.
3. Recognizing Debates and Contradictions: A good literature review doesn’t shy away from presenting opposing viewpoints and ongoing debates. Recognizing these tensions and contradictions can highlight unresolved questions or emerging concepts, guiding your own research focus.
4. Evaluating Strengths and Weaknesses of Existing Theories: Critically analyzing past research allows you to identify the strengths and limitations of existing theories. This helps you understand which theories are robust and applicable and which areas need further exploration, potentially leading to innovative approaches.
5. Building Upon Previous Work: The literature review allows you to see how different theories and concepts relate to each other and your research question. This knowledge helps you position your work within the existing conversation, building upon established ideas or introducing new ones.
Additional Tips
- Keyword Exploration: Utilize relevant keywords in your search queries to discover important theories and concepts associated with your topic.
- Author Tracking: Pay attention to frequently cited authors and influential figures in your field. Their work often reflects key theories and concepts.
- Consult Experts: Engage with professors, researchers, or librarians specializing in your field. They can provide guidance on prominent theories and suggest relevant sources.
- Conceptual Mapping: Visualize the relationships between concepts and theories you encounter through mind maps or diagrams. This aids in identifying key players and their connections.
What challenges might researchers face when conducting a literature review, and how can these be addressed
Conducting a robust literature review can be an enriching, yet challenging, experience for researchers. Here are some common hurdles and tips on how to overcome them:
1. Information Overload: With the vast amount of published research available, it can be overwhelming to identify, select, and manage relevant sources.
- Develop a focused research question: This helps refine your search terms and target specific areas within the broader field.
- Utilize advanced search techniques: Boolean operators, filters, and keyword variations can improve the precision of your search results.
- Leverage reference management tools: Software like Mendeley or Zotero help organize and annotate your findings efficiently.
2. Bias and Incomplete Coverage: Your search strategy and chosen sources might unintentionally introduce bias towards particular viewpoints or neglect relevant areas.
- Consult with librarians or research experts: They can offer guidance on diverse perspectives and alternative databases beyond the typical search engines.
- Seek out dissenting voices and alternative methodologies: Consider including research that challenges your initial assumptions to ensure a balanced review.
- Be transparent about limitations: Acknowledge potential biases and acknowledge areas where your review might be incomplete.
3. Difficulty Analyzing and Synthesizing Information: Turning information into meaningful insights can be challenging, especially when dealing with conflicting studies or complex concepts.
- Develop a clear analytical framework: This helps you categorize and evaluate studies based on specific criteria like methodology, theoretical perspectives, and findings.
- Identify key themes and arguments: Look for recurring patterns and contrasting viewpoints across different studies.
- Use critical thinking skills: Evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, and potential limitations of each study and its contribution to your understanding.
4. Time Constraints: Conducting a thorough literature review can be time-consuming, especially for students or researchers with limited resources.
- Develop a realistic timeline: Break down the review process into manageable steps and allocate sufficient time for each stage.
- Prioritize sources strategically: Focus on highly relevant and impactful studies initially, then expand your search as needed.
- Seek support from peers or mentors: Discuss your progress and challenges with others to stay motivated and receive feedback.
5. Access to Resources: Paywalled journals and limited library access can pose a barrier for some researchers, particularly those affiliated with smaller institutions.
- Explore open access resources: Numerous online platforms offer free access to scholarly articles and books.
- Utilize interlibrary loan services: Libraries can often borrow materials from other institutions for you.
- Network with other researchers: Share resources and potentially collaborate with colleagues who have access to different databases.
Conducting a well-structured and thoughtful literature review is an iterative process. Don’t be afraid to revisit your search terms, adjust your focus, and seek help when needed. By actively addressing these challenges, you can transform your literature review from a chore into a valuable tool for enriching your research project and enhancing its intellectual contribution.
How does a literature review help researchers avoid duplication of existing studies
A well-conducted literature review serves as a powerful tool for researchers to avoid duplication of existing studies in several ways;
1. Unveiling Existing Knowledge: By diligently exploring past research, researchers gain a comprehensive understanding of what has already been explored and established in their field. This knowledge enables them to identify areas where further investigation is truly needed, preventing them from replicating what’s already known.
2. Building Upon Previous Work: The literature review allows researchers to discover the strengths and weaknesses of past studies. This empowers them to build upon existing findings, addressing identified limitations or extending the investigation in new directions, rather than simply repeating previous efforts.
3. Identifying Gaps and Unanswered Questions: Through critical analysis of past research, researchers can pinpoint areas where knowledge is lacking or existing conclusions remain inconclusive. This guides them towards formulating original research questions that address these gaps and contribute novel insights to the field.
4. Recognizing Methodological Approaches: Examining methodologies employed in earlier studies helps researchers understand the effectiveness and limitations of specific methods. This knowledge allows them to adapt or design innovative approaches that avoid replicating potential flaws or inefficiencies in past studies.
5. Avoiding the “Reinventing the Wheel” Pitfall: By immersing themselves in the existing scholarship, researchers prevent themselves from unknowingly replicating established knowledge or methodologies. This saves valuable time and resources, allowing them to focus on truly innovative and impactful research contributions.
- Utilize systematic review techniques: These involve rigorous search strategies, selection criteria, and data analysis methods to ensure comprehensive coverage and minimize duplication.
- Consult research databases and tools: Many platforms offer features like citation analysis and duplicate detection to help researchers identify overlapping studies.
- Engage with experts and peers: Discussing your research topic and findings with experts or peers can help you identify areas where duplication might occur or suggest alternative directions for your study.
- Clearly define your research question: A well-defined research question ensures your study focuses on a specific gap in knowledge, minimizing the risk of unintentional duplication.
A literature review is not just about summarizing past research; it’s about critically evaluating it and using that knowledge to guide your own original contribution to the field. By diligently conducting your review and embracing its insights, you can avoid the pitfall of duplication and ensure your research makes a distinct and valuable impact.
In what ways does a literature review contribute to the theoretical framework of a research study
A literature review plays a crucial role in shaping and solidifying the theoretical framework of your research study in several key ways;
1. Identifying Relevant Theories and Concepts: Through your exploration of existing research, you’ll encounter prominent theories and concepts related to your topic. These serve as the building blocks for your own theoretical framework.
2. Understanding Established Explanations: The review exposes you to diverse theoretical explanations for the phenomena you’re investigating. This knowledge helps you understand the strengths, weaknesses, and limitations of existing explanations.
3. Selecting and Justifying Your Framework: Based on your understanding of existing theories and the specific focus of your research question, you can select the most relevant theories to form your theoretical framework. The literature review then serves as justification for your choice, demonstrating why these specific theories are best suited to address your research question.
4. Building Upon or Challenging Existing Theories: Depending on your findings, the literature review might support and contribute to established theories by providing new evidence or deeper insights. Alternatively, it might challenge existing theories by highlighting their limitations or offering alternative explanations.
5. Demonstrating Theoretical Coherence: Your literature review should showcase how the chosen theories connect with each other and how they collectively underpin your research question and methodology. This ensures a cohesive and well-reasoned theoretical framework.
6. Highlighting Originality and Significance: By clearly demonstrating how your theoretical framework builds upon, departs from, or refines existing theories, the literature review emphasizes the originality and potential significance of your research contribution.
- Clearly articulate your research question: This guides your search for relevant theories and ensures your framework directly addresses your specific inquiry.
- Engage in critical analysis: Don’t simply accept theories on face value. Evaluate their strengths, weaknesses, and internal consistency through the lens of your research question.
- Consult experts and peers: Discuss your chosen theories and their connection to your research with experts or peers for feedback and refinement.
- Maintain clear connections: Throughout your research, demonstrate how your findings relate back to your theoretical framework, illustrating its explanatory power and validity.
How can a comprehensive literature review help researchers contextualize their findings within the existing body of knowledge
A comprehensive literature review plays a crucial role in contextualizing research findings within the existing body of knowledge by serving several key functions:
1. Setting the Stage: The review provides a historical and theoretical background for your research topic. It establishes the current state of knowledge, key debates, and unresolved questions, creating a framework for understanding your findings.
2. Identifying Comparisons and Contrasts: By showcasing related research and its conclusions, the review allows you to compare your findings to existing knowledge. This highlights similarities, discrepancies, and novel contributions, demonstrating the significance of your study.
3. Explaining Your Results: You can leverage the review to explain your findings in relation to established theories and explanations. This strengthens the validity and generalizability of your conclusions by demonstrating how they fit within the larger picture.
4. Addressing Limitations and Implications: The review helps you identify the limitations of your study and acknowledge areas where further research is needed. It also allows you to discuss the potential implications of your findings for future research and practical applications.
5. Engaging in Scholarly Conversation: By referencing and critically analyzing previous studies, the review showcases your engagement with the existing scholarship. This positions you as a contributor to the ongoing conversation within your field.
- Maintain a Focus: While providing context, ensure your review remains focused on your specific research question and avoids irrelevant tangents.
- Integrate Findings Seamlessly: Weave your research findings into the review naturally, highlighting their unique contribution and connection to established knowledge.
- Acknowledge Different Perspectives: Don’t shy away from presenting contrasting viewpoints or alternative interpretations. This demonstrates a balanced and critical approach.
- Use Clear Language and Structure: Present your review in a way that is easy to understand and navigate for your target audience.
What role does a literature review play in identifying methodological approaches used in previous research studies
A literature review plays a crucial role in identifying methodological approaches used in previous research studies, serving as a foundation for designing your own methodology and demonstrating its significance. Here’s how;
1. Unveiling Existing Methods: By exploring studies relevant to your topic, you’ll discover the diverse methods employed by other researchers. This expands your understanding of how different research questions can be addressed through different methodologies.
2. Evaluating Strengths and Weaknesses: The review allows you to critically analyze the effectiveness and limitations of various methods used in past studies. This helps you understand the suitability of certain approaches for your specific research question and context.
3. Informing Your Choice: Based on your understanding of existing methods and the specific demands of your research question, you can make informed decisions about the most appropriate methodology for your study. This ensures your chosen approach aligns with both theoretical foundations and established practices.
4. Justifying Your Methodology: The literature review becomes a tool for justifying your chosen methods. By showcasing how your approach addresses limitations of past studies or offers a unique perspective, you demonstrate the suitability and potential advantages of your methodology.
5. Avoiding Pitfalls and Inefficiencies: Analyzing past methods helps you identify potential pitfalls or inefficiencies associated with specific approaches. This allows you to adapt existing methods or design new ones that avoid these weaknesses, leading to a more robust and efficient research process.
- Categorize Methods: Organize your findings by grouping similar methodological approaches or research designs. This helps you compare and contrast their applicability.
- Consider Your Research Question: Always evaluate methods through the lens of your specific research question and data needs. Don’t blindly mimic others; choose based on suitability.
- Consult Experts and Peers: Discuss your chosen methodology and its connection to your research question with experts or peers for feedback and refinement.
- Clearly Explain Your Choices: In your research report, clearly explain your chosen methodology, justifying it by referencing relevant past studies and highlighting its unique advantages.
How can a literature review help researchers identify potential sources of bias or limitations in existing studies
A literature review serves as a powerful tool for researchers to identify potential sources of bias and limitations in existing studies by offering several key perspectives;
1. Scrutinizing Design and Methodology: Examining research methods and design choices allows you to pinpoint potential sources of bias. Consider factors like sample selection, data collection procedures, and control groups. Look for imbalances, subjectivity, or lack of randomization that could skew results.
2. Evaluating Data Analysis and Interpretation: Analyze how studies handled data analysis and interpretation of findings. Look for selective reporting of data, subjective interpretations, or questionable statistical methods that might introduce bias or limit the validity of conclusions.
3. Identifying Conflicting Results and Gaps in Evidence: Comparing and contrasting findings across different studies can reveal inconsistencies or discrepancies. These conflicting results might point towards potential biases in specific studies or highlight limitations in the overall body of evidence.
4. Considering Author Bias and Research Context: Be aware of potential author biases related to funding sources, personal beliefs, or institutional affiliations. Examine the broader research context and prevailing discourses to identify potential biases shaping the field.
5. Consulting Quality Assessment Tools: Leverage established tools like the Cochrane Collaboration Risk of Bias tool or the PRISMA checklist to systematically assess the methodological quality of reviewed studies. These tools highlight potential weaknesses and limitations for further consideration.
- Develop a Critical Mindset: Approach your review with a questioning attitude, actively seeking potential flaws and limitations in methodology, analysis, and conclusions.
- Consult Experts and Peers: Discuss your findings and identified biases with experts or peers in your field. Their insights can help you refine your analysis and gain broader perspectives.
- Clearly Report Identified Biases: Don’t shy away from acknowledging and discussing potential biases in existing studies. This demonstrates transparency and strengthens your analysis.
- Use Your Findings to Guide Your Research: Identify and address limitations in previous studies by designing your research to overcome them. This contributes to a more robust and comprehensive understanding of your topic.
What impact does a thorough literature review have on the formulation of a research methodology
A thorough literature review can have a profound impact on the formulation of your research methodology by influencing several key aspects;
1. Identifying Relevant Research Designs: The review exposes you to diverse research designs used in previous studies related to your topic. This broadens your understanding of how specific questions can be addressed and helps you choose the most suitable design for your own research question.
2. Selecting Appropriate Data Collection Methods: By analyzing the methods used in past studies, you gain insights into the effectiveness and limitations of different data collection techniques. This knowledge empowers you to select methods that align with your research design and the type of data you need to answer your question.
3. Considering Sampling Strategies: Exploring how previous studies selected their samples allows you to assess the strengths and weaknesses of different sampling techniques. This informs your decisions regarding sample size, representativeness, and potential biases associated with different sampling strategies.
4. Developing Data Analysis Procedures: Reviewing past studies' analysis methods helps you understand different approaches to data processing, interpretation, and statistical techniques. This allows you to adapt or create appropriate analysis procedures tailored to your specific research question and data type.
5. Anticipating Potential Challenges: Analyzing the limitations and challenges encountered in past studies equips you to proactively address similar issues in your own research. This helps you refine your methodology and plan mitigation strategies to ensure data quality and validity.
6. Justifying Your Chosen Methods: The literature review becomes a foundation for justifying your chosen methods. By highlighting how your approach addresses limitations of past studies or offers a unique perspective, you demonstrate the suitability and potential advantages of your methodology.
- Focus on Methodological Relevance: When analyzing past studies, prioritize those that adopted research designs and methods closest to your own inquiry.
- Consult Experts and Peers: Share your chosen methodology and its connection to your research question with experts or peers for feedback and refinement.
- Maintain Rigor and Transparency: Ensure your chosen methods align with recognized research standards and clearly explain their rationale in your research report.
How does the literature review process contribute to the synthesis of information from various sources
The literature review process plays a crucial role in synthesizing information from various sources by several key mechanisms;
1. Critical Evaluation and Comparison: You don’t simply summarize each source individually; you actively compare and contrast their findings, methodologies, and theoretical perspectives. This helps you identify commonalities, inconsistencies, and unique contributions of each source.
2. Identification of Key Themes and Arguments: Through in-depth analysis, you uncover recurring themes, arguments, and concepts across different sources. This allows you to synthesize diverse information into a cohesive understanding of the overall knowledge landscape surrounding your topic.
3. Building Connections and Relationships: You go beyond just presenting findings side-by-side. You actively build connections between different sources, highlighting how they support, contradict, or expand upon each other’s ideas. This creates a richer and more nuanced understanding of the topic.
4. Integrating Theories and Explanations: You don’t just list theories; you evaluate their strengths and weaknesses within the context of your research question. By integrating relevant theories from different sources, you create a robust theoretical framework that informs your own research and analysis.
5. Constructing New Knowledge: Synthesis is not just about summarizing; it’s about drawing new insights and interpretations based on the combined information. By critically analyzing and creatively connecting across sources, you can formulate original perspectives and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
- Utilize Visual Tools: Mind maps, concept maps, or diagrams can help visualize relationships between different sources and key findings.
- Develop a Coding System: Categorize different sources based on themes, methodologies, or viewpoints to facilitate comparison and synthesis.
- Write Critically and Analytically: Don’t simply paraphrase; analyze, evaluate, and interpret the information from different sources in light of your research question.
- Maintain Transparency and Source Attribution: Clearly acknowledge the sources you use and ensure proper citation practices throughout your review.
By engaging in these active synthesis processes, the literature review becomes much more than a collection of summaries. It transforms into a powerful tool for generating new knowledge, refining your research question, and contributing meaningfully to the existing body of scholarship.
What strategies can researchers employ to critically evaluate and synthesize diverse literature in their field
Researchers can employ a variety of strategies to critically evaluate and synthesize diverse literature in their field;
Evaluation Strategies
- Scrutinize Methodology: Analyze the research design, sample selection, data collection, and analysis methods used in each source. Consider potential biases, limitations, and strengths of each approach.
- Evaluate Theoretical Frameworks: Examine the theoretical perspectives underpinning each study. Are they well-justified? Do they align with other studies and your own research question?
- Assess Findings and Claims: Don’t accept results at face value. Critically evaluate the evidence and arguments presented, considering alternative interpretations and potential counter-arguments.
- Consider Author Credibility: Look at the author’s expertise and publication history in the field. Are they respected figures? Do they have potential biases or conflicts of interest?
- Compare and Contrast Sources: Actively compare findings, methodologies, and conclusions across different sources. Identify similarities, discrepancies, and unique contributions of each study.
Synthesis Strategies
- Identify Recurring Themes and Arguments: As you analyze sources, look for common threads, concepts, and debates emerging across the literature. Organize your findings around these themes for clarity.
- Build Connections and Relationships: Don’t present sources in isolation. Highlight how they relate to each other, building a cohesive understanding of the topic. Show how they support, contradict, or expand upon each other’s ideas.
- Develop a Synthesis Framework: Create a structure to organize your synthesis, such as chronological analysis, thematic comparison, or methodological critique. This framework will guide your analysis and presentation.
- Integrate and Interpret: Go beyond simply summarizing. Use the combined information to draw new insights, interpretations, and conclusions relevant to your research question.
- Utilize Visual Tools: Mind maps, concept maps, or diagrams can help visualize relationships between sources, themes, and key findings.
- Consult Experts and Peers: Discuss your findings and interpretations with scholars or colleagues in your field. Their feedback can refine your analysis and identify potential blind spots.
- Utilize Specialized Tools: Software like NVivo or ATLAS.ti can help manage and analyze large amounts of literature data.
- Maintain Transparency and Citation: Clearly acknowledge the sources you use and ensure proper citation practices throughout your work.
- Focus on Quality Over Quantity: Don’t aim for an exhaustive review at the expense of depth. Prioritize high-quality, relevant sources that offer significant insights.

How does a literature review contribute to the identification of key variables and concepts in a research study
A well-conducted literature review plays a crucial role in identifying key variables and concepts for your research study in several ways;
1. Unveiling Relevant Domains and Theories: By immersing yourself in the existing scholarship, you’ll encounter various theories and concepts surrounding your topic. These serve as starting points for identifying potential variables relevant to your research question.
2. Identifying Relationships and Interactions: Through your analysis, you’ll discover how different concepts and variables are linked within existing studies. This helps you understand potential interactions and dependencies between factors you might investigate.
3. Examining Measurements and Operationalizations: Reviewing past research methods allows you to see how specific variables have been operationalized and measured. This informs your own choices regarding how to define and measure relevant variables in your study.
4. Recognizing Contextual Factors: The literature review exposes you to various contextual factors that might influence the variables you’re interested in. This awareness helps you identify potential moderator or control variables that need consideration in your research design.
5. Spotlighting Gaps and Untapped Potential: Analyzing past studies can reveal areas where specific variables haven’t been fully explored or their interactions haven’t been examined. This highlights opportunities for you to explore novel variables or investigate existing ones from a unique perspective.
- Develop a Focused Research Question: A clear and specific research question guides your search for relevant variables and ensures you don’t get overwhelmed by too much information.
- Utilize Key Terms and Search Operators: Explore the literature using relevant keywords and Boolean operators to refine your search and target specific concepts or variables.
- Consult With Experts and Peers: Discuss your research topic and potential variables with experts or colleagues in your field. Their insights can point you towards important concepts and suggest different perspectives.
- Conduct Thematic Analysis: Organize your findings by grouping related concepts and variables. This visualizes their connections and helps you identify key elements for your research.
- Maintain Theoretical Coherence: Ensure the identified variables and concepts align with your chosen theoretical framework, demonstrating their relevance to your research question.
The literature review is not just about passively collecting information; it’s about actively analyzing and making connections. By critically engaging with existing research, you’ll unearth the key variables and concepts that form the foundation of your study, ensuring its relevance, depth, and potential to add new knowledge to your field.
Can a literature review help researchers recognize trends and emerging themes in a particular academic field
Yes! A well-conducted literature review can be a powerful tool for researchers to recognize trends and emerging themes in a particular academic field. Here’s how;
1. Identifying Patterns and Recurring Concepts: As you delve into existing research, you’ll naturally start noticing recurring themes, ideas, and methodologies being employed across different studies. These patterns can point towards emerging trends gaining traction within the field.
2. Tracking Shifts in Focus and Emphasis: By comparing older studies with recent ones, you can identify shifts in the field’s focus. Are there new research questions gaining prominence? Are specific methodologies gaining favor? Recognizing these shifts can highlight emerging trends.
3. Analyzing Debates and Controversies: Examining ongoing debates and controversies within the literature can reveal areas where new knowledge is being actively sought. These discussions often point towards potential trends in the field as researchers explore various solutions or interpretations.
4. Recognizing Gaps and Unexplored Areas: A thorough literature review often uncovers gaps in previous research or areas where existing knowledge remains incomplete. Identifying these gaps can lead you to potential new trends as researchers strive to address them with their studies.
5. Utilizing Bibliometrics and Citation Analysis: Analyzing citation patterns and trends in publication dates can reveal which areas are attracting increasing attention and potential emerging trends that are gaining momentum within the field.
- Develop a Broad Search Strategy: Don’t limit yourself to specific journals or disciplines. Cast a wider net to capture diverse perspectives and identify potential trends across different subfields.
- Use Critical Analysis: Don’t simply accept trends at face value. Analyze their potential causes, implications, and validity. Are they supported by evidence, or are they merely hype?
- Consult Experts and Peers: Discuss your findings and interpretations with scholars or colleagues in your field. Their insights can help you confirm or refine your understanding of emerging trends.
- Consider the Broader Context: Analyze how emerging trends within your field connect with developments in other disciplines or societal changes. This adds context and depth to your understanding.
- Stay Updated: Regularly review new literature and attend conferences to keep informed of the latest developments and emerging trends in your field.
What is the significance of staying updated on the latest literature when conducting a literature review
Staying updated on the latest literature holds immense significance for conducting a thorough and impactful literature review in several ways;
1. Ensuring Comprehensiveness and Relevance: The field of research is constantly evolving, with new studies, methodologies, and theoretical frameworks emerging regularly. By incorporating the latest literature, you ensure your review encompasses the most current knowledge and findings, leading to a more comprehensive and relevant understanding of your topic.
2. Identifying Novel Research Questions and Gaps: Recent publications often highlight new areas of inquiry and potential shortcomings in existing knowledge. Staying updated helps you identify gaps in research and formulate innovative research questions that address these unresolved issues, contributing to the advancement of your field.
3. Avoiding Outdated Information and Biases: Relying solely on older literature might lead you to perpetuate outdated understandings or miss vital advancements that challenge previous biases. Staying updated ensures your review reflects the current state of knowledge and avoids misinterpretations based on superseded information.
4. Demonstrating Rigor and Expertise: Incorporating recent, high-quality studies into your review showcases your awareness of the latest developments and strengthens the credibility of your work. It demonstrates your commitment to conducting a thorough and well-informed analysis.
5. Fostering Collaboration and Networking: Engaging with the latest literature opens doors for collaboration with researchers exploring similar topics and methodologies. Utilizing new tools and platforms for scholarly communication allows you to connect with diverse perspectives and potentially contribute to ongoing research projects.
Strategies for Staying Updated
- Develop Targeted Alerts: Set up automatic notifications for new publications in relevant journals, databases, and author profiles.
- Attend Conferences and Workshops: Participate in academic events to gain insights into ongoing research and network with experts.
- Utilize Literature Review Tools: Leverage software like Mendeley or Zotero to efficiently manage your references and receive updates related to your research interests.
- Subscribe to Author Blogs and Newsletters: Follow prominent researchers in your field to stay informed about their latest work and insights.
- Join Online Communities and Forums: Engage in discussions with fellow researchers to share knowledge, exchange ideas, and learn about emerging trends.
Staying updated on the latest literature is not a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process. By actively engaging with new developments and incorporating them into your research, you can ensure your literature review remains relevant, impactful, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in your field.
How does the literature review process contribute to the overall rigor and validity of academic research
The literature review process plays a crucial role in ensuring the rigor and validity of academic research in several key ways;
1. Establishing Context and Foundation: A comprehensive literature review provides the context and theoretical foundation for your research. It demonstrates your understanding of the existing body of knowledge, relevant debates, and established methodologies. This ensures your research isn’t conducted in isolation and builds upon existing knowledge, contributing to the overall understanding of your field.
2. Preventing Duplication and Redundancy: By thoroughly exploring past research, you can identify areas where research is already saturated and avoid replicating what has already been done. This prevents unnecessary duplication of effort and ensures your research focuses on addressing genuine gaps in knowledge.
3. Justifying Your Research Question and Methodology: The literature review allows you to justify the significance of your research question and the chosen methodology. You can demonstrate how your study addresses limitations in previous research, offers unique insights, or employs innovative approaches, ultimately contributing to the advancement of knowledge.
4. Identifying Potential Biases and Limitations: A critical analysis of existing research helps you identify potential biases and limitations in previous studies. By acknowledging these limitations and outlining strategies to address them in your own research, you demonstrate awareness and enhance the trustworthiness of your findings.
5. Ensuring Transparency and Traceability: The literature review showcases the sources and evidence upon which your research is built. This transparency allows other researchers to assess the validity of your arguments, replicate your findings, and build upon your work, contributing to the overall scientific process.
6. Building Credibility and Expertise: A well-researched and well-presented literature review showcases your understanding of the field and your ability to critically evaluate existing knowledge. This establishes your credibility as a researcher and strengthens the impact of your findings.
7. Enhancing Argumentation and Communication: Your knowledge gleaned from the literature review enriches your arguments by providing them with historical context, theoretical underpinnings, and comparisons to related work. This improves communication and ensures your research resonates with other scholars in the field.
8. Informing Data Analysis and Interpretation: By understanding how past research has approached similar topics, you can develop a more informed approach to analyzing your own data and interpreting your findings. This helps you ensure your conclusions are well-grounded and supported by existing knowledge.
Tips for developing academic writing skills
What are the 5 parts of the research paper
How do I write a research paper
How to incorporate data and statistics in research papers
What are the steps for writing a research paper
How to prepare a research paper outline
How to write a research paper outline
How to write a research paper
A Guide to Literature Reviews
Importance of a good literature review.
- Conducting the Literature Review
- Structure and Writing Style
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Citation Management Software This link opens in a new window
- Acknowledgements
A literature review is not only a summary of key sources, but has an organizational pattern which combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
The purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
- << Previous: Definition
- Next: Conducting the Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Jul 3, 2024 3:13 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mcmaster.ca/litreview
Matada Research

Understanding the importance of a literature review in research
- March 29, 2023

Gerald Naepi
When conducting research, a literature review plays a crucial role as it provides an overview of the existing literature related to a specific topic. Its main objective is to identify the gaps in the current knowledge and provide direction for future research. This article delves into the purpose and structure of a literature review, along with the various types of literature reviews typically employed in research. By familiarising themselves with the different types of literature reviews and their unique features, researchers can determine which review type would best suit their research question and help them achieve their desired results.
Purpose of a literature review in research
The primary goal of a literature review in research is to offer a comprehensive overview of the relevant research within a given area. A well-executed literature review should provide readers with a clear understanding of the theoretical and empirical contributions made in the field, while also highlighting areas that require further exploration or investigation. Additionally, literature reviews help researchers identify gaps in existing knowledge that can lead to new hypotheses or questions for future study.
When conducting a literature review, researchers should pay close attention to key themes and topics covered by previous studies, including the approaches used to answer specific questions or address particular issues. This ensures that any conclusions drawn by the researcher are supported by established evidence and build on prior work in the field. Moreover, when synthesising information from multiple studies, researchers should aim to identify conflicting opinions or discrepancies in the literature and draw implications for further study. Through this process, a comprehensive literature review can provide invaluable insights into the current state of research and inform future studies.

Literature review format
The format of a literature review in research typically consists of the following elements:
Introduction: The introduction is an important part of a literature review, as it gives the reader a sense of what to expect. It should start with a clear statement of the research question or objective, so that the reader understands what the review is trying to achieve. It’s also important to explain why the topic is important, so that the reader understands the relevance of the review. Finally, the introduction should give the reader an overview of the structure and organisation of the review, so that they can easily navigate through the rest of the content.
Search Strategy: The search strategy should be comprehensive, focused, and systematic. It involves selecting appropriate databases, developing effective search terms, and utilizing other sources to collect information. To begin, the researcher needs to determine the most relevant databases to search. Depending on the topic, discipline, and research question, different databases may be more suitable. Some commonly used databases are PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. Once the databases are selected, the researcher can develop a set of search terms that accurately reflect the topic and research question. These search terms can be a combination of keywords and subject headings. Other sources of information may include reference lists, grey literature, conference proceedings, and experts in the field. These sources can provide additional insights and help to ensure a comprehensive search.
The search strategy should be documented in detail to enable replication and transparency. This documentation should include the databases searched, search terms used, search dates, and any filters or limits applied. By having a clear and systematic search strategy, the researcher can ensure that they have identified all relevant literature and that the research findings are reliable and valid.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria: Inclusion criteria refer to the characteristics that a study must have to be included in the review, while exclusion criteria refer to the characteristics that disqualify a study from being included. The inclusion and exclusion criteria may vary depending on the research question, but generally, they should be clearly defined and stated in the methods section of the review. Common criteria include study design, population, intervention or exposure, and outcome measures. For example, a systematic review on the effectiveness of a particular drug for a specific condition may include only randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with a minimum sample size of 50 participants, and exclude non-randomized studies or studies with a high risk of bias.
Defining clear inclusion and exclusion criteria is crucial in ensuring that the studies included in the review are relevant, appropriate, and of high quality. It also helps to minimize bias and enhance the validity of the review’s findings. Additionally, transparent reporting of inclusion and exclusion criteria allows readers to assess the rigor of the review process and the generalizability of the findings to their own context.
Methodology: The methodology section typically involves outlining the procedures and techniques employed to collect relevant data and information, including any data extraction forms that were used. Additionally, this section may also include information about the process of data extraction, such as how the data was collected, coded, and analysed. Furthermore, it is essential to include a description of the quality assessment process used to ensure that the extracted data was reliable and valid. This may involve explaining the criteria used to evaluate the quality of the studies, as well as any potential biases or limitations that were taken into consideration. By providing a thorough description of the methodology, readers will be able to assess the rigor of the research and better understand the context and implications of the findings.
Results: The results section summarises the main outcomes and findings of the review process, including the key themes, concepts, and trends identified in the literature. The results section provides a clear and concise description of the analysed data and should be presented in a logical and organized manner to make it easy for readers to understand. The results section of a literature review provides an overview of the evidence and information obtained from the analysed sources and explains how the findings support or challenge the research question or hypothesis. It is essential to ensure that the results are presented accurately, and any limitations or weaknesses of the study are acknowledged to provide a transparent and objective review of the literature.
Discussion: The discussion section of a literature review in research is an important component that provides a critical analysis of the literature reviewed in the study. This section allows the researcher to present their findings and interpretations of the literature, as well as to draw conclusions about the research question or problem being investigated. In the discussion section, the researcher will typically summarise the key findings of the literature review and then discuss these findings in relation to the research question or problem. The discussion section may also identify gaps in the literature and suggest areas for further research, as well as discuss the implications of the findings for theory, practice, or policy. Ultimately, the discussion section of a literature review should provide a comprehensive and insightful analysis of the literature reviewed, which contributes to the overall understanding of the research question or problem at hand.
Conclusion: The conclusion section in a literature review summarises the key findings and implications of the reviewed studies. It is the final part of the literature review that brings together all the main points and themes discussed in the previous sections. In this section, the researcher should provide a critical evaluation of the reviewed literature, highlighting the strengths and limitations of the studies, and how they relate to the research question or problem. The conclusion section should also address any gaps or inconsistencies in the existing literature and suggest future research directions. Furthermore, it should provide a clear and concise summary of the main findings and their significance for the field of study.
References: The reference section provides a comprehensive list of all the sources that have been cited in the literature review, including books, journal articles, reports, and other relevant materials. The purpose of the reference section is to give credit to the authors whose work has been used to support the arguments and ideas presented in the paper. Additionally, the reference section allows readers to locate and retrieve the sources that have been cited, which can help them further explore the topic or verify the accuracy of the information presented. The reference section is typically organized in alphabetical order by the last name of the first author of each source, and it includes all of the necessary bibliographic information such as the title of the work, the name of the journal or book, the date of publication, and the page numbers
Download our literature review template

Types of literature review in research
Literature reviews in research can be conducted for a variety of reasons, including to gain a comprehensive understanding of a topic, to identify research gaps, or to support the development of research proposals.
Here are the different types of literature reviews in research:
- Narrative Literature Review: A narrative literature review is an overview of the literature on a specific topic or research question that does not follow a structured or systematic approach. It is a qualitative review that summarizes and synthesizes the findings from different studies.
- Systematic Literature Review: A systematic literature review is a rigorous and structured approach to reviewing literature that involves a comprehensive search strategy, inclusion/exclusion criteria, and critical appraisal of the quality of evidence. It involves a meta-analysis and quantitative synthesis of data from multiple studies.
- Meta-analysis: A meta-analysis is a quantitative review of the literature that involves statistical analysis of the data from multiple studies. It combines the results of different studies to produce an overall estimate of the effect size of a particular intervention or treatment.
- Scoping Review: A scoping review is a type of literature review that aims to map the existing literature on a topic, identify research gaps, and provide an overview of the evidence. It is useful when the research question is broad or unclear.
- Rapid Review: A rapid review is a type of systematic review that uses streamlined methods to quickly and efficiently review the literature. It is useful when there is a time constraint or when there is a need to update a previous review.
- Umbrella Review: An umbrella review is a type of systematic review that synthesizes the findings of multiple systematic reviews on a particular topic. It provides a higher level of evidence by combining the findings from multiple studies.
- Critical Review: A critical review involves the evaluation and analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the literature on a particular topic. It assesses the quality, credibility, and relevance of the literature and identifies research gaps.
Literature review example:
A literature review can play a crucial role in connecting with qualitative talanoa research. Talanoa is a research approach that emphasises collaboration, dialogue, and relationships within Pacific communities. Conducting a thorough literature review can help researchers to identify existing knowledge and gaps in ta specific field. This can inform the design of Talanoa research that centers on community engagement and dialogue. By reviewing literature that focuses on Pacific cultures, histories, and knowledge systems, researchers can develop a deeper understanding of the context and values of the community they are working with. This can help to build trust and establish meaningful relationships between researchers and community members.
An example of a literature review is our social research on Pacific peoples’ concerns about COVID-19, titled “The $7 cabbage dilemma: Pacific peoples’ experiences and New Zealand’s COVID-19 response.pdf” The objective of our study was to investigate how the COVID-19 pandemic impacted the wellbeing of Pacific peoples in New Zealand. To accomplish this, we conducted a comprehensive literature review of existing research on Pacific peoples’ urban climate change, health, economy, and housing in New Zealand. Through our talanoa-based research, we discovered that many Pacific peoples were worried about the cost of living, access to healthcare, support for parents, and affordable healthy food options, which were all connected to the broader themes of urban climate change, health, economy, and housing that we had identified in our literature review.
In conclusion, a literature review is an essential component of research as it helps to identify gaps in existing knowledge, provide direction for future research and support or challenge research questions or hypotheses. The purpose of a literature review is to offer a comprehensive overview of the relevant research within a given area, identify key themes and topics, and synthesize information from multiple studies. Researchers need to pay attention to the different types of literature reviews and their unique features when conducting literature reviews to determine which review type would best suit their research question and help them achieve their desired results. A well-structured literature review should include an introduction, search strategy, inclusion and exclusion criteria, methodology and results sections. A well-executed literature review ensures that the research findings are reliable and valid and provides invaluable insights into the current state of research to inform future studies.
Checkout our Pinterest for the infographic

Matada is a social enterprise that specializes in transformative research, evaluation, consultation, knowledge dissemination and program development to improve the health and wellbeing of communities in Aotearoa New Zealand. Our mission is to create solutions that enhance the wellbeing of individuals, communities, and society. We are backed by highly qualified and experienced researchers with both international and domestic experience. We lead with core values (relationships, respect, reciprocity, community and service) that shape our goals and vision which helps us create positive change.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
By: Gerald Naepi
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
What is the Purpose of a Literature Review?

4-minute read
- 23rd October 2023
If you’re writing a research paper or dissertation , then you’ll most likely need to include a comprehensive literature review . In this post, we’ll review the purpose of literature reviews, why they are so significant, and the specific elements to include in one. Literature reviews can:
1. Provide a foundation for current research.
2. Define key concepts and theories.
3. Demonstrate critical evaluation.
4. Show how research and methodologies have evolved.
5. Identify gaps in existing research.
6. Support your argument.
Keep reading to enter the exciting world of literature reviews!
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a critical summary and evaluation of the existing research (e.g., academic journal articles and books) on a specific topic. It is typically included as a separate section or chapter of a research paper or dissertation, serving as a contextual framework for a study. Literature reviews can vary in length depending on the subject and nature of the study, with most being about equal length to other sections or chapters included in the paper. Essentially, the literature review highlights previous studies in the context of your research and summarizes your insights in a structured, organized format. Next, let’s look at the overall purpose of a literature review.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Literature reviews are considered an integral part of research across most academic subjects and fields. The primary purpose of a literature review in your study is to:
Provide a Foundation for Current Research
Since the literature review provides a comprehensive evaluation of the existing research, it serves as a solid foundation for your current study. It’s a way to contextualize your work and show how your research fits into the broader landscape of your specific area of study.
Define Key Concepts and Theories
The literature review highlights the central theories and concepts that have arisen from previous research on your chosen topic. It gives your readers a more thorough understanding of the background of your study and why your research is particularly significant .
Demonstrate Critical Evaluation
A comprehensive literature review shows your ability to critically analyze and evaluate a broad range of source material. And since you’re considering and acknowledging the contribution of key scholars alongside your own, it establishes your own credibility and knowledge.
Show How Research and Methodologies Have Evolved
Another purpose of literature reviews is to provide a historical perspective and demonstrate how research and methodologies have changed over time, especially as data collection methods and technology have advanced. And studying past methodologies allows you, as the researcher, to understand what did and did not work and apply that knowledge to your own research.
Identify Gaps in Existing Research
Besides discussing current research and methodologies, the literature review should also address areas that are lacking in the existing literature. This helps further demonstrate the relevance of your own research by explaining why your study is necessary to fill the gaps.
Support Your Argument
A good literature review should provide evidence that supports your research questions and hypothesis. For example, your study may show that your research supports existing theories or builds on them in some way. Referencing previous related studies shows your work is grounded in established research and will ultimately be a contribution to the field.
Literature Review Editing Services
Ensure your literature review is polished and ready for submission by having it professionally proofread and edited by our expert team. Our literature review editing services will help your research stand out and make an impact. Not convinced yet? Send in your free sample today and see for yourself!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your ...
"A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research". Boote and Baile 2005 . Authors of manuscripts treat writing a literature review as a routine work or a mere formality. But a seasoned one knows the purpose and importance of a well-written literature review.
Importance of a Literature Review. There are various reasons for carrying out literature review. Majorly, literature review helps in: ... A researcher usually uses secondary data for literature review. Some of the major and widely used sources for literature reviews include articles in professional journals, statistical data from government ...
Important reminders. A literature review is indispensable across various industries because it provides a comprehensive understanding of existing research, identifies gaps, and lays the groundwork for new studies. It ensures that research efforts are not duplicated and promotes the advancement of knowledge. It also offers a well-informed basis ...
It can also help to provide an overview of areas in which the research is disparate and interdisciplinary. In addition, a literature review is an excellent way of synthesizing research findings to show evidence on a meta-level and to uncover areas in which more research is needed, which is a critical component of creating theoretical frameworks and building conceptual models.
The literature review holds paramount importance in academic writing for several reasons. Firstly, it serves as a comprehensive survey of existing research, establishing a solid foundation for the author's work. It helps identify gaps, trends, and debates in the chosen field, guiding researchers toward relevant and valuable contributions.
A literature review is not only a summary of key sources, but has an organizational pattern which combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem.
The primary goal of a literature review in research is to offer a comprehensive overview of the relevant research within a given area. A well-executed literature review should provide readers with a clear understanding of the theoretical and empirical contributions made in the field, while also highlighting areas that require further exploration or investigation.
A literature review is a critical summary and evaluation of the existing research (e.g., academic journal articles and books) on a specific topic. It is typically included as a separate section or chapter of a research paper or dissertation, serving as a contextual framework for a study. Literature reviews can vary in length depending on the ...
Beyond the important role literature reviews serve in the broader research process, this short commentary reflects on three additional benefits we gained from writing our literature review, namely: doing rigorous interdisciplinary research; writing for non-academic audiences; and working together with new collaborators.