

How to Write a Great Business Case
Explore more.
- Case Teaching
C ase studies are powerful teaching tools. “When you have a good case, and students who are well prepared to learn and to teach each other, you get some magical moments that students will never forget,” says James L. Heskett, UPS Foundation Professor of Business Logistics, emeritus, at Harvard Business School (HBS). “They will remember the lessons they learn in that class discussion and apply them 20 years later.”
Yet, for many educators who want to pen their own case, the act of writing a great business case seldom comes easily or naturally. For starters, it’s time consuming. Case writers can spend substantial time visiting companies, securing a willing site, conducting interviews, observing operations, collecting data, reviewing notes, writing the case, revising the narrative, ensuring that teaching points come through, and then getting executives to approve the finished product.
The question, then, becomes: Where do you begin? How do you approach case writing? How do you decide which company to use as the subject of the case? And what distinguishes a well-written case from a mediocre one?
We asked three expert HBS case writers—who collectively have written and supported hundreds of cases—to share their insights on how to write a great business case study that will inspire passionate classroom discussion and transmit key educational concepts.
Insights from James L. Heskett
UPS Foundation Professor of Business Logistics, Emeritus, Harvard Business School
Keep your eyes open for a great business issue.
“I’m always on the prowl for new case material. Whenever I’m reading or consulting, I look for interesting people doing interesting things and facing interesting challenges. For instance, I was reading a magazine and came across a story about how Shouldice Hospital treated patients undergoing surgery to fix inguinal hernias—how patients would get up from the operating table and walk away on the arm of the surgeon.
6 QUALITIES OF GREAT CASE WRITERS
Comfort with ambiguity, since cases may have more than one “right” answer
Command of the topic or subject at hand
Ability to relate to the case protagonists
Enthusiasm for the case teaching method
Capacity for finding the drama in a business situation and making it feel personal to students
Build relationships with executives.
“When writing a case, it’s helpful to start as high in the organization as possible. It helps assure mid-level managers that they can share the information you need with an outsider. It also helps when it comes to getting the case cleared for use. Serving on corporate boards can help in building relationships with senior executives, but there are other ways to make those connections. For instance, you can approach speakers at business conferences if you think their presentations could form the basis for a good business case. If you want to write about a company where you don’t have any personal connections, you can always check with your colleagues to see if any of them have a personal relationship with the CEO or sit on a board where they could introduce you to the right person who would be able to facilitate the case. My colleagues and I make a lot of these introductions for each other.”
“If you make the case into a crossword puzzle that takes five hours to solve, it’s not really fair to the students and will most likely cause them to lose focus.” James L. Heskett
Skip the curveballs and focus on key issues.
“Cases don’t have to be obvious. As a pedagogical objective, you might want students to look beyond a superficial issue to say this is the underlying topic that we need to address, and these are the questions we need to pose. Still, I think it’s unhelpful if cases contain real curveballs where ‘unlocking’ the case depends on finding some small piece of information hidden in an exhibit. Give students a break! They may have to read and digest three cases per day, so they probably won’t be able to devote more than a couple of hours to each one. If you make the case into a crossword puzzle that takes five hours to solve, it’s not really fair to the students and will most likely cause them to lose focus.”
Build a discussion plan while writing the case.
“In case method teaching, the teacher is not in complete control. Students teach each other and learn from each other. On any given day, there will likely be somebody in the room who knows more about the company featured in the case than the professor does. So a professor can’t walk into the classroom and expect to impose a lesson plan that goes in a strict linear way from A to B to C to D. The case ought to be written to allow students to jump from A to D and then come back later to B if that’s how the discussion plays out. At the same time, the case should be structured so that the instructor can collect student comments on a board, organizing them as a coherent set of related ideas, and then deliver a 5-to-10-minute summary that communicates whatever essential concepts the case has covered. This summation can be a very powerful teaching and learning experience.”
Focus on quality over quantity.
“Cases don’t have to be too long. Some good cases are only two or three pages. Students may give more scrutiny to these brief cases than they would a 20-page case.”
Advice from Benson P. Shapiro
Malcolm P. McNair Professor of Marketing, Emeritus, Harvard Business School
Take out the chaff in advance.
“You don’t want students to spend too much time separating the wheat from the chaff. If a case has 12 pages of text and 10 pages of exhibits, even the smartest MBA students will likely lose interest. Writers who try to capture a situation from every angle and in every detail end up with sprawling narratives that usually do not make a good case. When writing cases, you need to set good, strong boundaries. Avoid superfluous, flowery, or poetic material that may contain interesting anecdotes or factoids, but that could distract readers from the case’s core topics. Include only those important and useful details that can help students make decisions and understand key issues that the case explores.”
Work in layers and metaphors—subtly.
“The best cases work on multiple levels. A case should focus on a specific situation—for example, whether or not to introduce a certain product. But it should also serve as a metaphor for broader issues in the background: How do we think about introducing new products? Are we introducing enough products? Are new product introductions a source of competitive advantage in our industry? How should we organize and manage new product development? You want the case to encourage students to think broadly about the various cultural, financial, and strategic impacts that managerial decisions have on a company.”
“Writers who try to capture a situation from every angle and in every detail end up with sprawling narratives that usually do not make a good case.” Benson P. Shapiro
Encourage emotional engagement.
“Case writing is an interesting literary form—it needs to be very engaging, but also educational. Great cases revolve around points of contention on which intelligent people can hold different points of view: What should you do? Why? How do you get it done? Ideally, students should have to choose between two very attractive alternatives or two terrible alternatives. The best cases involve questions that get students emotionally engaged so that they really care about choices and outcomes. When you see students physically leaning forward and following what their peers are saying, you know that they have a visceral feel for the importance of the subject. When you hear them debating after class— You were out in left field! You missed what was really important here! —that’s how you can tell you succeeded in developing a great case.”
Lessons from Carin-Isabel Knoop
Executive Director of the Case Research & Writing Group, Harvard Business School
Don’t forget the classroom component.
“Cases are deliberately incomplete documents. What a case writer leaves out of a case is often just as important as what he or she puts into it. Cases are designed to be completed through classroom instruction and discussion. While drafting the case, try to develop the classroom process in parallel. Work on the assignment questions and classroom content. Keep in mind that the case should be able to adapt to your classroom and course needs.”
Hone your elevator pitch.
“Before getting started, always have clear, succinct learning objectives in mind. Don’t start developing the case until you are able to summarize these objectives in less than five minutes.”
Case writing is a relationship, not a transaction.
When choosing a case site, be clear with executives that you are developing a teaching tool and that you will require their time and candor—and eventually their data. Put them at ease, and manage the authorization process, right from the start. Indicate that quotes will be cleared before publication and there will be time for individual review. During the creation process, ask their advice. This creates a process of engagement and helps bring home that this is a pedagogical tool, not gotcha journalism. At HBS, we oftentimes invite someone from the company to attend class. Finally, once the case is done, stay in touch with your case protagonists. They will move to other organizations and spread the good word about their experience with case writing.
Invite disagreement in case discussions.
“The case study method is based on participant-centered learning. The students all start from the same base of 11 (or however many) pages in the case, but they bring different knowledge and experiences into the classroom. So they can take the same facts and disagree about what course of action to pursue. We want students to behave like decision makers, and it can be painful to make decisions. Some critics deride the case teaching method as being unrealistic, but someone who just lectures about marketing doesn’t help students realize how difficult it is to choose between two plausible options to meet the same marketing objectives. For students, a big part of the education process is learning from discussions with classmates who think differently and advocate for different solutions. Witnessing a robust case discussion reminds us of the potential for collective learning to emerge from contrasting views.”
“Faculty don’t just write cases for teaching purposes, they write them to learn.” Carin-Isabel Knoop
The Case Writing Process Is a Worthy Effort
Researching, writing, and publishing cases is well worth the time and effort. “The case research and writing process is important for faculty development,” Knoop adds. “While developing field cases, faculty go to site visits and meet with decision makers. The case writing process helps connect scholars to practitioners and practitioners to the academic world. Faculty case writers get to explore and test how their academic theories work in practice. So faculty don’t just write cases for teaching purposes, they write them to learn. The case method is an integral part of faculty development.”
There’s another big bonus to becoming a case writer, especially for younger educators. “Young business instructors face a credibility gap with their students,” says Heskett. “It’s not uncommon to have MBA students in a class who have more experience than the instructor on a particular subject. Once you go into the field and write a case, you will know more about that subject than anyone else in the class. A primary way for professors to establish their credibility on a topic is to have written the case the class is discussing that day.”

James L. Heskett is UPS Foundation Professor of Business Logistics, emeritus, at Harvard Business School. He completed his Ph.D. at the Graduate School of Business, Stanford University, and has been a faculty member at The Ohio State University as well as president of Logistics Systems, Inc. Since 2000, he has authored a blog on Harvard Business School’s Working Knowledge website .

Benson P. Shapiro is the Malcolm P. McNair Professor of Marketing, emeritus, at Harvard Business School where he taught full time from 1970 to 1997. Since 1997, Shapiro has concentrated his professional time on consulting, giving speeches, serving on boards, and writing. He continues to teach at Harvard and has taught in many executive programs and has chaired the Sustainable Marketing Leadership for Mid-Sized Firms Program.

Carin-Isabel Knoop is the executive director of the Case Research & Writing Group at Harvard Business School. She is also coauthor of Compassionate Management of Mental Health in the Modern Workplace .
Related Articles
Need a coauthor for your next business case study, what happens when you assign a case in a different language, 5 tips to get your case class talking.
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
- Contact sales
Start free trial
How to Write a Business Case (Template Included)

Table of Contents
What is a business case, business case template, how to write a business case, key elements of a business case, how projectmanager helps with your business case, watch our business case training video.
A business case is a project management document that explains how the benefits of a project outweigh its costs and why it should be executed. Business cases are prepared during the project initiation phase and their purpose is to include all the project’s objectives, costs and benefits to convince stakeholders of its value.
A business case is an important project document to prove to your client, customer or stakeholder that the project proposal you’re pitching is a sound investment. Below, we illustrate the steps to writing one that will sway them.
The need for a business case is that it collects the financial appraisal, proposal, strategy and marketing plan in one document and offers a full look at how the project will benefit the organization. Once your business case is approved by the project stakeholders, you can begin the project planning phase.
When Should You Write a Business Case?
Around 70 percent of businesses that survive longer than five years follow a strategic business plan. And every project an organization undertakes should demonstrate real business value via a business case. A business case is created during the initiation phase of a project. At this point, the project is being conceptualized and evaluated on what the potential return on investment could be. The business case document helps determine the project’s needs and allows decision-makers to determine if the project aligns with the organization’s strategic goals.
For example, a business case may be used when there’s a new project proposal, when entering into a new market, when upgrading software solutions or when there’s a major capital expenditure. Once the business case has been approved, the project will move to the planning phase.
Why Is It Important to Write a Business Case Document?
A business case document benefits projects for several reasons.
- Justifies why a project is needed, outlining costs, benefits and risks
- Engages stakeholders and gets their buy-in and support
- Allows decision-makers to assess feasibility and make choices based on data
- Provides estimates for costs, resources and timelines to improve resource allocation
- Helps hold teams accountable for delivering on commitments
Overall, it helps guide the project initiation and execution to result in thoughtful and strategic decisions.
Our business case template for Word is the perfect tool to start writing a business case. It has 9 key business case areas you can customize as needed. Download the template for free and follow the steps below to create a great business case for all your projects.
Projects fail without having a solid business case to rest on, as this project document is the base for the project charter and project plan. But if a project business case is not anchored to reality, and doesn’t address a need that aligns with the larger business objectives of the organization, then it is irrelevant.
The research you’ll need to create a strong business case is the why, what, how and who of your project. This must be clearly communicated. The elements of your business case will address the why but in greater detail. Think of the business case as a document that is created during the project initiation phase but will be used as a reference throughout the project life cycle.
Whether you’re starting a new project or mid-way through one, take time to write up a business case to justify the project expenditure by identifying the business benefits your project will deliver and that your stakeholders are most interested in reaping from the work. The following four steps will show you how to write a business case.
Step 1: Identify the Business Problem
Projects aren’t created for projects’ sake. They should always be aligned with business goals . Usually, they’re initiated to solve a specific business problem or create a business opportunity.
You should “Lead with the need.” Your first job is to figure out what that problem or opportunity is, describe it, find out where it comes from and then address the time frame needed to deal with it.
This can be a simple statement but is best articulated with some research into the economic climate and the competitive landscape to justify the timing of the project.
Step 2: Identify the Alternative Solutions
How do you know whether the project you’re undertaking is the best possible solution to the problem defined above? Naturally, prioritizing projects is hard, and the path to success is not paved with unfounded assumptions.
One way to narrow down the focus to make the right solution clear is to follow these six steps (after the relevant research, of course):
- Note the alternative solutions.
- For each solution, quantify its benefits.
- Also, forecast the costs involved in each solution.
- Then figure out its feasibility .
- Discern the risks and issues associated with each solution.
- Finally, document all this in your business case.
Step 3: Recommend a Preferred Solution
You’ll next need to rank the solutions, but before doing that it’s best to set up criteria, maybe have a scoring mechanism such as a decision matrix to help you prioritize the solutions to best choose the right one.
Some methodologies you can apply include:
- Depending on the solution’s cost and benefit , give it a score of 1-10.
- Base your score on what’s important to you.
- Add more complexity to your ranking to cover all bases.
Regardless of your approach, once you’ve added up your numbers, the best solution to your problem will become evident. Again, you’ll want to have this process also documented in your business case.

Get your free
Use this free Business Case Template for Word to manage your projects better.
Step 4: Describe the Implementation Approach
So, you’ve identified your business problem or opportunity and how to reach it, now you have to convince your stakeholders that you’re right and have the best way to implement a process to achieve your goals. That’s why documentation is so important; it offers a practical path to solve the core problem you identified.
Now, it’s not just an exercise to appease senior leadership. Who knows what you might uncover in the research you put into exploring the underlying problem and determining alternative solutions? You might save the organization millions with an alternate solution than the one initially proposed. When you put in the work on a strong business case, you’re able to get your sponsors or organizational leadership on board with you and have a clear vision as to how to ensure the delivery of the business benefits they expect.
One of the key steps to starting a business case is to have a business case checklist. The following is a detailed outline to follow when developing your business case. You can choose which of these elements are the most relevant to your project stakeholders and add them to our business case template. Then once your business case is approved, start managing your projects with a robust project management software such as ProjectManager.
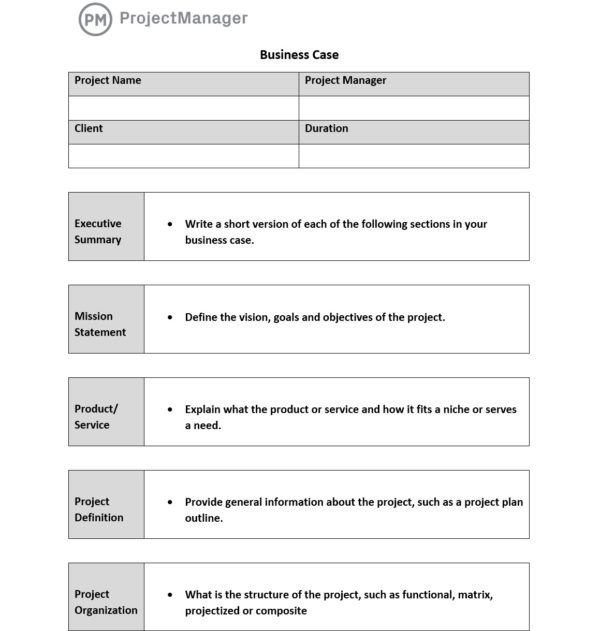
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is a short version of each section of your business case. It’s used to give stakeholders a quick overview of your project to help them understand the project’s purpose, benefits and implications. Some components of an executive summary include the project overview, business need, proposed solution to the need, cost estimate, return on investment, risks, timeline and a call to action.
2. Project Definition
This section is meant to provide general information about your projects, such as the business objectives that will be achieved and the project plan outline. It offers a comprehensive overview of the project including its objectives and scope. Here, include details such as the objectives, stakeholders, scope, expected outcomes and constraints.
3. Vision, Goals and Objectives
First, you have to figure out what you’re trying to do and what is the problem you want to solve. You’ll need to define your project vision, goals and objectives. This will help you shape your project scope and identify project deliverables.
4. Project Scope
The project scope determines all the tasks and deliverables that will be executed in your project to reach your business objectives. Think of it as establishing the project’s boundaries to help stakeholders better understand what to expect. A well-defined scope can also improve resource allocation and project planning, two key factors of the project’s long-term success.
5. Background Information
Here you can provide a context for your project, explaining the problem that it’s meant to solve, and how it aligns with your organization’s vision and strategic plan.
6. Success Criteria and Stakeholder Requirements
Depending on what kind of project you’re working on, the quality requirements will differ, but they are critical to the project’s success. Collect all of them, figure out what determines if you’ve successfully met them and report on the results .
7. Project Plan
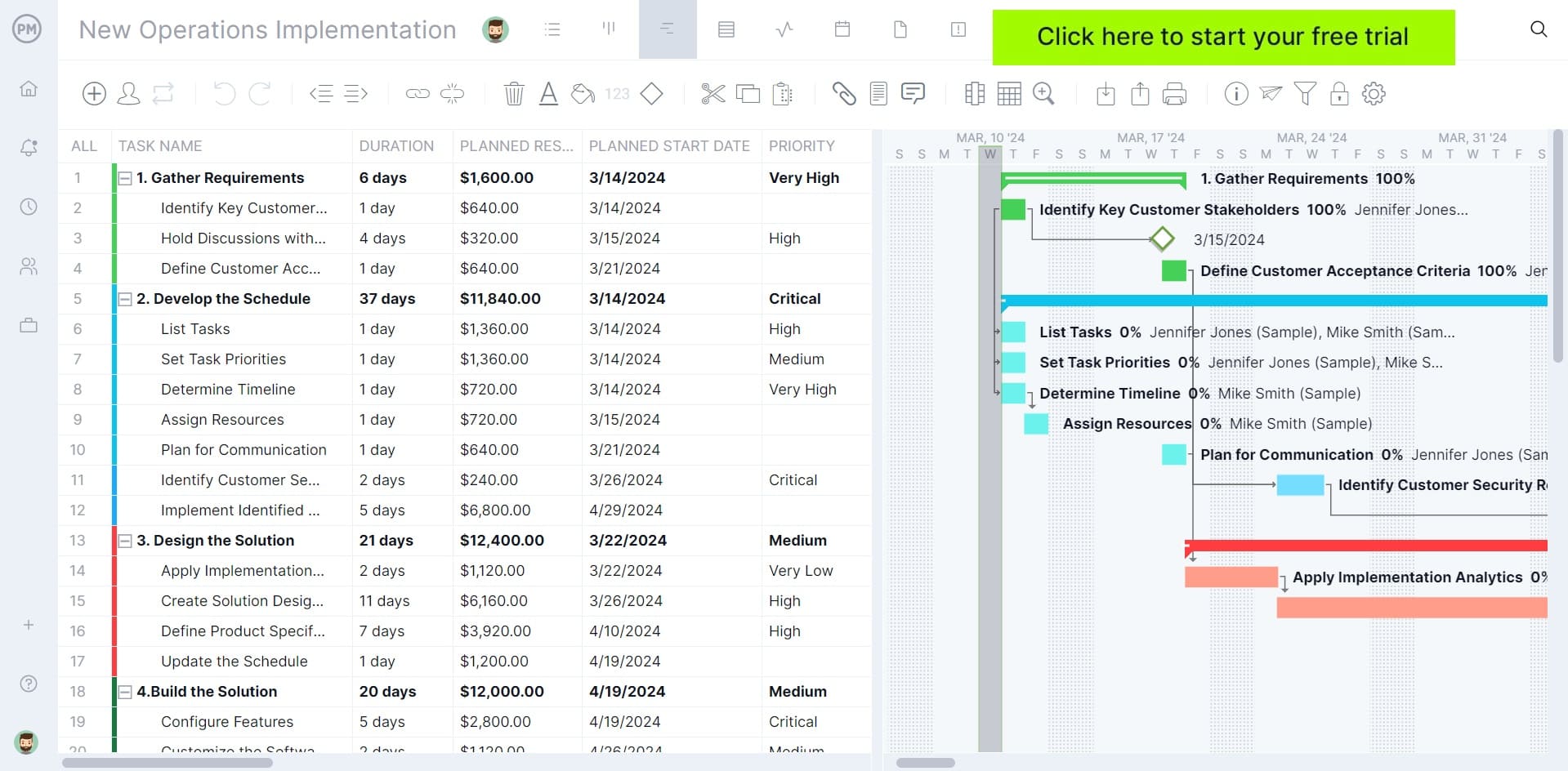
It’s time to create the project plan. Figure out the tasks you’ll have to take to get the project done. You can use a work breakdown structure template to make sure you are through. Once you have all the tasks collected, estimate how long it will take to complete each one.
Project management software makes creating a project plan significantly easier. ProjectManager can upload your work breakdown structure template and all your tasks are populated in our tool. You can organize them according to your production cycle with our kanban board view, or use our Gantt chart view to create a project schedule.
8. Project Budget
Your budget is an estimate of everything in your project plan and what it will cost to complete the project over the scheduled time allotted. It outlines the financial resources such as personnel costs, software or hardware costs, consulting fees, training costs and contingency funds. It also provides the return on investment information and shows how the benefits will outweigh the costs.
9. Project Schedule
Make a timeline for the project by estimating how long it will take to get each task completed. For a more impactful project schedule , use a tool to make a Gantt chart, and print it out. This will provide that extra flourish of data visualization and skill that Excel sheets lack.
10. Project Governance
Project governance refers to all the project management rules and procedures that apply to your project. For example, it defines the roles and responsibilities of the project team members and the framework for decision-making.
11. Communication Plan
Have milestones for check-ins and status updates, as well as determine how stakeholders will stay aware of the progress over the project life cycle. The communication plan can help foster an atmosphere of transparency and engagement among stakeholders. The plan outlines how, when and what will be communicated so that everyone is informed and on the same page.
12. Progress Reports
Have a plan in place to monitor and track your progress during the project to compare planned to actual progress. There are project tracking tools that can help you monitor progress and performance.
Again, using a project management tool improves your ability to see what’s happening in your project. ProjectManager has tracking tools like dashboards and status reports that give you a high-level view and more detail, respectively. Unlike light-weight apps that make you set up a dashboard, ours is embedded in the tool. Better still, our cloud-based software gives you real-time data for more insightful decision-making. Also, get reports on more than just status updates, but timesheets, workload, portfolio status and much more, all with just one click. Then filter the reports and share them with stakeholders to keep them updated.

13. Financial Appraisal
This is a very important section of your business case because this is where you explain how the financial benefits outweigh the project costs . Compare the financial costs and benefits of your project. You can do this by doing a sensitivity analysis and a cost-benefit analysis.
14. Market Assessment
Research your market, competitors and industry, to find opportunities and threats. The market assessment can also help outline the overall market condition and how that could impact the project. For example, what are the current market needs and trends? Are there any barriers to entry that could impact the project such as strong competition or high capital requirements? Note all of this information in this section of the business case.
15. Competitor Analysis
Identify direct and indirect competitors and do an assessment of their products, strengths, competitive advantages and their business strategy. For example, how does each competitor position itself in the market? What pricing strategy do they implement and where is there room for differentiation? Then, use this information to help guide future decisions.
16. SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis helps you identify your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. The strengths and weaknesses are internal, while the opportunities and threats are external. This is a structured approach to help stakeholders make more informed decisions and outlines how to better leverage internal and external resources. The SWOT analysis helps ensure that the project aligns with organizational goals and market conditions.
17. Marketing Strategy
Describe your product, distribution channels, pricing, target customers among other aspects of your marketing plan or strategy.
18. Risk Assessment
There are many risk categories that can impact your project. The first step to mitigating them is to identify and analyze the risks associated with your project activities. From there, you can assess the likelihood and impact of each and rank them based on this information. The risk assessment makes it easier to focus on the most pressing risks and includes a mitigation strategy to reduce the impact in case the risk comes to fruition.
ProjectManager , an award-winning project management software, can collect and assemble all the various data you’ll be collecting, and then easily share it both with your team and project sponsors.
Once you have a spreadsheet with all your tasks listed, you can import it into our software. Then it’s instantly populated into a Gantt chart . Simply set the duration for each of the tasks, add any dependencies, and your project is now spread across a timeline. You can set milestones, but there is so much more you can do.
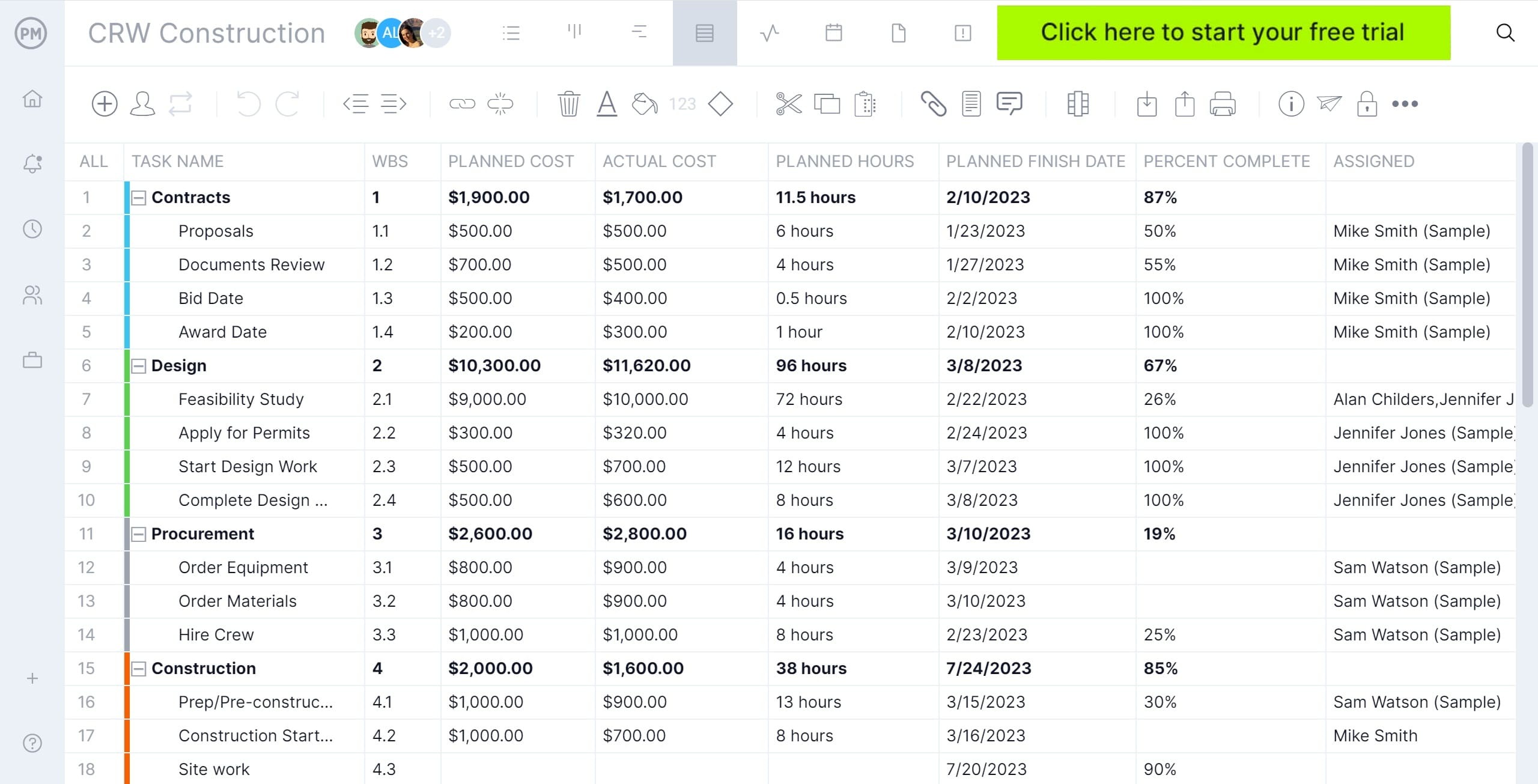
You have a project plan now, and from the online Gantt chart, you can assign team members to tasks. Then they can comment directly on the tasks they’re working on, adding as many documents and images as needed, fostering a collaborative environment. You can track their progress and change task durations as needed by dragging and dropping the start and end dates.
But that’s only a taste of what ProjectManager offers. We have kanban boards that visualize your workflow and a real-time dashboard that tracks six project metrics for the most accurate view of your project possible.
Try ProjectManager and see for yourself with this 30-day free trial .
If you want more business case advice, take a moment to watch Jennifer Bridges, PMP, in this short training video. She explains the steps you have to take in order to write a good business case.
Here’s a screenshot for your reference.

Transcription:
Today we’re talking about how to write a business case. Well, over the past few years, we’ve seen the market, or maybe organizations, companies or even projects, move away from doing business cases. But, these days, companies, organizations, and those same projects are scrutinizing the investments and they’re really seeking a rate of return.
So now, think of the business case as your opportunity to package your project, your idea, your opportunity, and show what it means and what the benefits are and how other people can benefit.
We want to take a look today to see what’s in the business case and how to write one. I want to be clear that when you look for information on a business case, it’s not a briefcase.
Someone called the other day and they were confused because they were looking for something, and they kept pulling up briefcases. That’s not what we’re talking about today. What we’re talking about are business cases, and they include information about your strategies, about your goals. It is your business proposal. It has your business outline, your business strategy, and even your marketing plan.
Why Do You Need a Business Case?
And so, why is that so important today? Again, companies are seeking not only their project managers but their team members to have a better understanding of business and more of an idea business acumen. So this business case provides the justification for the proposed business change or plan. It outlines the allocation of capital that you may be seeking and the resources required to implement it. Then, it can be an action plan . It may just serve as a unified vision. And then it also provides the decision-makers with different options.
So let’s look more at the steps required to put these business cases together. There are four main steps. One, you want to research your market. Really look at what’s out there, where are the needs, where are the gaps that you can serve? Look at your competition. How are they approaching this, and how can you maybe provide some other alternatives?
You want to compare and finalize different approaches that you can use to go to market. Then you compile that data and you present strategies, your goals and other options to be considered.
And then you literally document it.
So what does the document look like? Well, there are templates out there today. The components vary, but these are the common ones. And then these are what I consider essential. So there’s the executive summary. This is just a summary of your company, what your management team may look like, a summary of your product and service and your market.
The business description gives a little bit more history about your company and the mission statement and really what your company is about and how this product or service fits in.
Then, you outline the details of the product or service that you’re looking to either expand or roll out or implement. You may even include in their patents may be that you have pending or other trademarks.
Then, you want to identify and lay out your marketing strategy. Like, how are you gonna take this to your customers? Are you going to have a brick-and-mortar store? Are you gonna do this online? And, what are your plans to take it to market?
You also want to include detailed information about your competitor analysis. How are they doing things? And, how are you planning on, I guess, beating your competition?
You also want to look at and identify your SWOT. And the SWOT is your strength. What are the strengths that you have in going to market? And where are the weaknesses? Maybe some of your gaps. And further, where are your opportunities and maybe threats that you need to plan for? Then the overview of the operation includes operational information like your production, even human resources, information about the day-to-day operations of your company.
And then, your financial plan includes your profit statement, your profit and loss, any of your financials, any collateral that you may have, and any kind of investments that you may be seeking.
Related Project Planning Content
- Project Documentation: 15 Essential Project Documents
- How to Create a Project Execution Plan (PEP)
- How to Write a Scope of Work
So these are the components of your business case. This is why it’s so important. And if you need a tool that can help you manage and track this process, then sign up for our software now at ProjectManager .

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.
- eSignatures
- Product updates
- Document templates
How to write a business case study: your complete guide
Hanna Stechenko Manager, SEO Management
- Copy Link Link copied
Business case studies are powerful tools for marketing, teaching, and training. They help to create valuable learning experiences that can be shared with others.
A well-written business case study can also generate leads, increase customer loyalty, and boost sales.
But writing an effective and compelling case study can be easier said than done.
Great case studies aren’t something that you can write by yourself.
You’ll need help from existing clients who are willing to talk about their problems publicly, and you’ll need to safeguard their reputation while you tell their story.
It’s tricky.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at how to write a business case study, including best practices, case study templates, real examples, and more.
Let’s jump in.
What is a business case study?
A business case study is an in-depth look at a specific company or organization that examines how a business solved a problem, achieved success, or faced failure.
Case studies are often used by businesses to demonstrate the effectiveness of their strategies and solutions.
They can also serve as inspiration for other organizations that may be considering similar approaches.
The idea is simple: Stakeholders evaluating a product may be able to see the value of that product by learning how other companies have tried and succeeded with it.
For that reason, 42% of marketers still list case studies as a top media format used to generate leads and sales.
Strong case studies are often based on interviews with actual customers to highlight the effectiveness of a specific feature, explain a certain use case, or emphasize benefits or results of note.
Done correctly, a case study combines customer testimonials, process information, and usage data to tell a unique story about how a product or service helped a company succeed.
That’s why case studies are sometimes known as customer success stories.
What makes a strong case study?
Before we jump into the details of how to make a great case study, let’s take a closer look at what a strong case study actually looks like.
To create a great case study, you’ll need each of the following:
- Clear, compelling storylines. A good case study should include a clear story line that conveys the problem, solution, and the impact of the solution.
- A strong presentation of data. Demonstrate how your product or service has made an impact on the customer’s business with documented facts and figures.
- Credible client testimonials. Include feedback from real clients and users about how your product or service solved their issue. With permission, use a person’s real name and job title and personal experience to add credibility to your case study.
- Streamlined visuals. Graphics, photos, charts and/or videos can help illustrate results in an engaging and easy to understand way.
- Call to action. Always include a link to more information or a contact form at the end of your case study.
While all of these components are essential to great case studies, they aren’t always easy to acquire. Be prepared to dig for information and work closely with customers to build compelling content.
Why use case studies at all?
Great case studies can take some time to create.
Considering budgets and deadlines, why should you even bother using them when you could create more landing pages, buy more ads, or write more blog posts?
It’s a fair point to consider.
Case studies come with a unique set of benefits for your marketing strategy that other forms of content simply can’t fill.
1. They can last a long time
A single case study can be used as sales and marketing collateral as long as the feature products or services are still relevant.
If your products have a long lifespan, the same piece of content may be useful for months or years.
2. They’re relatively inexpensive
Case studies are relatively inexpensive to produce compared to other forms of marketing, such as white papers, e-books, and long-form blog content.
3. They drastically boost your credibility
Done correctly, case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of your products and services from the perspective of customers who have benefited directly from using them.
In a sense, case studies represent your products and services through the eyes of customers who have already taken the proverbial leap of faith.
When speaking to prospects and leads who aren’t fully bought in, they can minimize risk and offer assurances in a way that no other piece of sales and marketing collateral can match.
With all of that preliminary information out of the way, let’s take a closer look at how to actually build an effective case study.
Before you start: Understanding stakes and obstacles
The strongest case studies are usually created in collaboration between two companies: Your organization and that of a current or former customer with whom you have a good relationship.
At a high level, the process is straightforward:
- Question creation . Your team compiles a list of interview questions designed to tell a compelling story for new, prospective customers.
- Interview. Your team interviews a representative or stakeholder from the customer-partner organization.
- Draft. After the interview is complete, your team transforms the interview into a complete narrative.
- Feedback round. The customer-partner reviews the draft and provides feedback and input.
- Final draft. Your team makes corrections based on that feedback and resubmits for final approval.
- Final approval. The customer-partner approves the draft.
- Publish. Your team creates marketing collateral and publishes or shares the case study.
Simple, right?
Unfortunately, the process is rarely this smooth.
There are several outlying factors that can stop your case in its tracks or prevent it from ever seeing the light of day.
Here are some factors that you’ll need to consider before you start the case study process.
1. Relationship
Potential interview targets are more likely to agree to an interview if they have a strong relationship with someone on your team, like an account manager or a longtime sales rep.
Without a way to get your foot in the door, your interview request may be politely declined.
2. Availability
People are busy.
It’s not uncommon for the interval between reviews and approvals to take weeks at a time.
Because case study drafts need to be approved by both parties, expect delays while your drafts are circulated through your partner organizations.
3. Branding
Even if your product or service helped an organization overcome a huge obstacle, they may not want to talk about that weakness in a public forum.
Many companies are very cautious about anything that portrays their brand in an unfavorable light.
4. Legality
If your customer-partner doesn’t like what you’ve written, they may simply forbid you to use their name, logos, or data as part of your case study.
Moving forward without their permission could cause legal issues and damage customer relationships.
5. Approval
Sometimes, it’s impossible to get final approvals from the appropriate individuals in the customer-partner organization.
If HR or legal needs to sign off on the final product before it can be officially released, it could take weeks or months before that final approval comes through.
Above all else, remember: The customer-partner that agrees to help you create a case study is doing you a favor.
Most of the time, the customer-partner receives no benefit from the time and effort spent creating this piece.
They can’t use it to sell their own services, and they may reveal information and data that demonstrates a weakness in their management or internal process.
Keep that information in mind as you select your customer partners.
Be sure to treat these partners with care and respect, as a bad case study experience can damage a healthy customer relationship.
Step 1: Planning and prep
Business case studies will usually fall under the domain of your marketing team, but you’ll need to be specific when assigning project tasks and responsibilities.
Here’s what you need in order to create a case study:
- Internal project stakeholder. This individual oversees the project internally. They assign tasks, handle outreach, and oversee the production and delivery of the case study.
- External project stakeholder. The individual at the customer organization who agrees to help. This person may or may not be the individual who is interviewed by your organization.
- Interviewer. The individual who conducts the interview.
- Writer. The individual who writes the case study.
- Project manager. The individual who manages the case study project and ensures that deadlines are met.
- Internal editor or approver. The individual who reviews the case study and provides feedback or final approvals.
- External editor or approver. The individual at the customer organization who reviews the case study and provides feedback or final approvals.
- Designer. The individual who formats the case study, provides data-based graphics and illustration, or produces the final product file (typically a PDF or web page) with the case study and all relevant content.
Sometimes, these roles are combined.
The internal project stakeholder may also manage the product and provide editorial feedback after the case study is written.
Or, if you’re working with a freelancer for this process, they may conduct the interview, write the draft, and furnish a final design.
Next, consider your goals:
- Why are you writing this case study? Do you have a specific goal, such as boosting lead generation or improving customer lifetime value (CLV)?
- If your case study is angled to grow business with existing customers, you may select different features from case studies meant to introduce prospective customers to your products.
- This could include add-on services or premium product features.
- Do you have any new products, services or updates you’d like to share with the world?
- Do you have a new positioning strategy?
After you’ve defined your objectives, it’s time to start considering who you might want to interview.
1. Make your list specific
Include the company name, any relevant notes and the name of the intended stakeholders to be interviewed.
2. Only include notable candidates
Make sure that your interview targets have experienced substantial or notable results with your product.
Look for clients who have experienced exceptional and transformative outcomes while using your product or service.
3. Consider existing relationships
Look for clients that already have a strong working relationship with you.
If they regularly work with an account manager or are in constant contact with specific team members, consider bringing those individuals into the conversation early.
Once you have your targets, reach out, explain your project, and see if the customer is interested in participating.
When you ask for an interview, be sure to mention the following details:
- The purpose of the case study and what you’re ultimately trying to accomplish.
- A brief overview of the case study process (including the interview process and what happens next).
- Timeframes and estimated deadlines.
- A general idea of the kinds of questions they may be asked.
- Explain scenarios for how and where the case study may be used (you’ll need their permission to share it with your audiences).
- Thank them for their time.
If they agree, start scheduling your timeline.
Work backwards from the date you’d like to publish, then build in dates for reviews and edits. Also create a flexible internal deadline for securing a client interview.
Since you’ll need to align your schedule with that of your interviewee, pinpointing an actual interview date can take some time.
Step 2: The interview process
As we mentioned above: Most of the time, the customer-partner that agrees to help you with your case study receives no major benefit from the project.
It helps you, but it doesn’t usually help them.
With that in mind, your goal during the interview process is to make things as easy, streamlined, and stress-free as possible.
One major step that you can take to calm nerves and prevent misunderstandings is to send an interview questionnaire prior to your interview.
This will help your customer-partner understand your main objectives and prepare their responses in advance.
Here are a few sample questions you might use:
- How many team members use our product/service? Which departments?
- What were your challenges before using our product/service/process?
- What made you leave your previous solution for our product?
- How do you use our product/service/process?
- What features or tools have been the most helpful for your business?
- If you asked us for help, how did we provide you with what you need? We’d like to understand this from your perspective.
- How have you benefited from our offering–and what have been your greatest results to date? Please provide specific metrics, if possible.
- What surprised you most about using our product/service/process?
- How have your customers or clients benefited from your use of our products or services?
- Is there anything else you would like us to know?
When you sit down to interview the client, it’s easiest to follow the interview questions that you sent over and simply record their responses.
However, don’t just stick to the script during the actual interview . Listen and actively engage with your interviewee.
Ask follow-up questions. Clarify details. Explore the answers in real time with your interviewee.
Use the opportunity to dig deeper and gather all the information you need to tell the right story to your prospects and leads.
You might also use a tool like Otter.ai to record and capture the transcript at the same time, but be sure to have your customer-partner sign a recording permission release if you intend to use sound bytes from that recording as part of your final case study.
Step 3: Writing your business case study
Ideally, the interview is the last piece of information you need before writing your case study.
All of the background information and preliminary work should be done as part of the interview preparation.
When you finish speaking with the customer-partner, it’s time to consolidate your notes and write the draft.
Before you begin, take a moment to review your overall objectives and the story that you want to tell. From there, select a format for your case study and start the draft.
Regardless of the modules, headings, or illustrations that you use, the case study should cover what life was like before the customer started using your product or service and what happened after they adopted those products/services into their workflow.
Sample case study outline
1. introduction.
A brief description of the case study’s contents (bullet point key metrics and successes).
2. Company overview
A brief description of the featured company — what they do, who their customers are, what they sell, etc. Include brief background/context as to how they use your product, service or process.
3. Problem / Challenge
Describe the business problem or opportunity that your customer was facing before they started using your product or service.
Include strong quotes and fully illustrate why the issue was a problem that needed to be solved.
4. Solution
Explain how the customer used your product to solve their problem.
Share their decision-making process, how they arrived at your solution, what convinced them to purchase, and how they implemented that solution internally.
Share benefits and features that stood out to them. Reinforce these details with quotes from your interview.
Summarize the outcome from the customer’s implementation of your product, service, or process.
Recap their wins, as well as the major improvements that they have seen over both the short and long term.
Add data and metrics, where relevant. Include quotes about how the current solution empowers the company and solves their problems.
6. About us
Share a brief explanation of your company and the products or services you provide.
7. Call-to-action (CTA)
Add a call to action with the appropriate contact information (or a contact button, if this is a web-based case study) so that users can get in touch for additional information after reading the case study.
When it’s time to start writing, gather all relevant information and relevant links (white papers, other case studies, sales and spec sheets, etc.) to make sure you have access to the full scope of information related to the products and services mentioned in your case study.
Your goal isn’t to overload the reader by explaining everything. Instead, focus on creating a benefits-driven story around the features that your products and services provide.
Use data and details to provide precise information at key points.
It’s likely that you will need to bridge the information gap between your interviewee and your target audience.
Since your clients know you understand your product or service, they’re likely to answer your questions in broader terms.
However, your readers will not be as familiar with your organization and may only have limited experience with what you sell.
Instead, you’ll need to provide context as you write. If your business has buyer personas or ideal customer profiles (ICP), it’s a great idea to keep those on hand.
It’s also important to reserve enough writing time to get creative. Thoughtfully work your way through your materials to come up with the type of angle that will make your case study worthwhile.
Best practices
- Start with an attention-grabbing, relevant headline.
- Avoid lengthy explanations unless you’re working on a more complex case study.
- If you’re writing a business case study that’s complicated because of the subject matter or necessary background information, consider starting the content with an executive summary to improve readability.
- Only include a table of contents for lengthier case studies.
- Write in the third person.
- Avoid alienating your readers by assuming they’ll understand technical details. Skip the jargon and explain every acronym to hold their attention the entire way.
- A good business case study is a story. Make sure it has a strong beginning, middle, and end. A conversational tone often works best.
- Keep it focused. Don’t highlight a million wins for a single case study. Pick one or two combinations of challenges and solutions instead. If you include more, you might dilute your message or bore your readers.
- Always include direct quotes for an added dose of personality, energy, and human connection.
- Include stats or metrics whenever possible, such as increased revenue, the number of new customers gained, or a measurable boost in traffic.
- If you’re in a very visual industry like graphic design, advertising, fashion, or interior design, include on-brand images where relevant.
- Standard case study length: Roughly 500-1000 words.
- Long-form case study: Roughly 1500-2000 words.
- Make your customer-partner the hero. While your products and services are key to customer success, they are ultimately there to aid the customer in the important work that they do.
Revise and review
Once you’ve completed your case study draft, take a few minutes to re-read everything and ensure that the draft tells the right story.
- Double-check that all facts and figures are correct.
- Set it aside for a time and get some distance. Return to the draft with a fresh perspective.
- Pass it to your colleagues, including internal stakeholders and approvers, for feedback.
- Provide enough details and context so that readers can see customer benefits and how your solution can help them succeed.
Seek client approval
When you’re satisfied with your case study, it’s time to send a copy of the draft to your client for their review and approval.
This is an important step in ensuring maximum transparency and visibility.
Your customer partner should know exactly what you plan to share and have enough time to share it with key stakeholders from their marketing and/or legal department.
It is highly likely that your customer-partner will request changes.
Some changes may be simple (such as clarifying job roles), but others may be more drastic.
Your customer partner may request that you remember sensitive data and details or phrase issues in a more favorable light.
Most organizations seek to avoid bad press and prefer not to point out key weaknesses in their internal processes and strategies.
Be prepared to soften your language or advocate to keep key data points in place.
This is often one of the most critical parts of the case study process. Proceed with caution and choose your battles wisely.
While you can push back on suggested changes, remember that your customer-partner can rescind the use of their name and information in your case study.
Though you can choose to publish anyway (with names and titles omitted), your case study would be far less influential as a result.
Regardless of the potential gains from a case study, it’s not worth poisoning a relationship with a customer that actively uses and promotes your product.
Step 4: Marketing your case study
When you have the finished product, it’s time to share and promote your case study. Think about using these channels:
- A dedicated landing page.
- The resources section of your website.
- Your company blog.
- One or a series of marketing emails.
- Social media.
- Custom infographic.
Requiring readers to fill out a short online form to get the download may allow sales and marketing teams to connect with potential leads.
If you do go the gated route, be sure the conditions of opting in are crystal clear. And feature a couple of non-gated case studies on your site for everyone who’d prefer to skip the forms.
Regardless of how you market your case study, don’t forget about your sales team!
Sales reps will get a lot of use out of your case studies.
They can feature them as links in their email signatures and include them in sales emails and proposals for new clients and potential customers.
Ready to get started? Try out this case study presentation template .
Good case study examples (and why they work)
If you’re struggling with case studies, you can find plenty of great examples around the internet.
Start reading well-executed case studies to learn more about what makes them work.
Below, you’ll find a selection of three very different but successful case studies.
PandaDoc case study
Intro : Before diving into the body of the case study, we briefly introduced the company, TPD, and highlighted three major metrics for a promising start.
The problem: We quickly engaged readers with our conversational tone. We also invited them to walk in TPD’s shoes through empathetic language and relatable context.
Challenges, solutions, and results: We took readers on a storytelling journey to help our case study flow. We gave them enough information to understand the “why”, but never bogged them down with unnecessary details. We were also sure to include supporting quotes and specific, measurable results in these critical sections.
Pull quote: We reserved the very best quote as the only pull quote, ensuring it would receive the attention it deserves.
Format: Finally, every time we mentioned a new company, we gave it a hyperlink to help readers save time.
Trello case study
Unicef + trello: helping others when they need it most.
Facts and figures : Trello opens the case study with great at-a-glance information, sharing insights into UNICEF as an organization and their relationship with Trello products.
Challenges, solutions, and results: This case study takes readers through a detailed narrative, providing statistics and metrics whenever possible. Readers are immersed into the story of exactly how UNICEF used Trello to help thousands of people during a natural disaster, offering enough detail to spark use case inspiration for other Trello users.
Photos: Trello included photos of actual UNICEF employees working remotely around the globe. The pictures gave the case study a personal feel, which could help readers better identify with the story.
Readers are reminded of the unique challenges of working together while apart to start considering how Trello might be able to help them find the solutions they need. Remember, the best case studies are relatable to all of your prospects!
Format: Its structure makes this longer case study easy to read. Sections of text are kept short while bullet points and pull quotes provide visual breaks.
Finally, hyperlinks to organizations’ websites open in separate tabs to help prevent losing case study readers along the way.
Stripe case study
Simplepractice launches automatic payments offering for clinicians with stripe.
Intro: In just two sentences, Stripe successfully manages to explain what SimplePractice is, what they offer, who they serve, how they serve them, and the benefits those clients gain.
While it’s not necessary to be this brief, readers will be more likely to read your entire intro if it’s on the shorter side.
Sidebar : The sidebar draws eyes to keep reading with two impressive metrics and a brightly-hued CTA button to “contact sales”.
Challenge and solution: These sections read like a story, with each sentence enticing the reader to continue to the next. It’s also great that a quote from SimplePractice’s COO is used to add context, emphasizing the gravity of their challenge.
Results: Stripe gives a lot of detail here for a strong close to the case study. After explaining how their offering brought ease to SimplePractice’s business, they went on to share detailed specifics on what made things easier and in what ways.
They also explained how their offering improved the businesses of SimplePractice’s clients. It’s highly persuasive for readers to understand they have the opportunity to not only benefit their own companies but also those of their clients.
Pull quote: The case study ends with a strong pull quote in a can’t-miss-it color.
Format: Stripe has a great case study format.
Wrapping up
The truth is: No matter how much you talk up your product, you’re a biased participant in any conversation. You have an ulterior motive, and that makes any direct claims you make about your product or service questionable.
Why? Because you want to sell your product!
Case studies offer an alternative way to soften your messaging by allowing prospects and potential buyers to hear from the people who use your products in real-world, everyday situations.
By placing your customers and their experiences at the front of your marketing, you can use trust and relatability to bridge a gap in a way that numbers and data just can’t provide.
Your customers already have great stories about how your solutions have transformed the work that they do.
Help them speak and share those stories with the people who need to hear them most with a case study.
Good luck? Be sure to check out other marketing tips and tricks on the PandaDoc blog .
Frequently asked questions
What is the best business case study format.
The best business case study format depends on the nature of the results and what you’re trying to achieve. You can figure that out by carefully reviewing your customer success stories and interviews.
- What stands out the most?
- What are you trying to achieve?
- How can you use your layout to guide readers through your story?
- What is your industry or what is the industry of your featured client?
Pro tip : Some interviews are more quotable than others. If you have too many great quotes to include them in your featured sections, consider adding a few pull quotes to your layout.
How do I create a business case study outline?
To create a business case study outline, list all of your featured sections and use bullet points to note subsections and what should be covered.
Most case studies feature the following sections:
- Introduction
- Brief Description of Customer’s Business
- Problem/Challenge/Opportunity
- Results/Conclusion
- About Us / Boilerplate
- Call-to-Action (CTA).
But outlines aren’t just for traditional case studies. Use outlines to guide your infographic and video versions too.
What are some case study best practices?
Best practices for writing case studies include:
- Crafting short, easy-to-digest sections.
- Weaving in a narrative for engaging storytelling.
- Starting with an engaging headline.
- Writing in layman’s terms.
- Explaining any necessary acronyms.
- Including any supporting metrics or statistics.
- Using direct quotes to bring your customer’s story to life.
Also, be sure to get the approval of your client and their marketing team after you’ve had time to review your first draft and fact-check all information.
Where can I find a good case study design template?
You can find a good case study design template on PandaDoc.
Our company’s expertise is spot-on and the case study templates are free. Also, don’t be afraid to branch out. Let’s say you have a big following on YouTube or Spotify.
You might want to create a video or podcast version of your case study for readers who prefer audiovisual information.
Or, you may want to add multimedia content to your case study, such as a video insert or or audio clip.
PandaDoc is not a law firm, or a substitute for an attorney or law firm. This page is not intended to and does not provide legal advice. Should you have legal questions on the validity of e-signatures or digital signatures and the enforceability thereof, please consult with an attorney or law firm. Use of PandaDocs services are governed by our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Originally published October 27, 2022, updated March 30, 2023
Streamline your document workflow & close deals faster
Get personalized 1:1 demo with our product specialist.
- Tailored to your needs
- Answers all your questions
- No commitment to buy
- Fill out the form
- Book a time slot
- Attend a demo
By submitting this form, I agree that the Terms of Service and Privacy Notice will govern the use of services I receive and personal data I provide respectively.
Related articles

Proposals 13 min

Proposals 14 min

Proposals 12 min
- Strategy Templates
Consulting Templates
- Market Analysis Templates
- Business Case

- Consulting Proposal
- Due Diligence Report

All Templates
How to write a solid business case (with examples and template).

Table of contents
What is a business case, business case vs. business plan, how to structure your business case, how to write a business case.
- Business Case PowerPoint template
ROI calculator template
- Key elements of a strong Business Case
Frequently asked questions
Nearly every new project requires approval—whether it's getting the green light from your team or securing support from executive stakeholders. While an informal email might suffice for smaller initiatives, significant business investments often require a well-crafted business case. This guide, written by former consultants from McKinsey and Bain, will help you write a compelling business case. It provides the steps and best practices to secure the necessary support and resources for a successful project.
A business case is a written document (often a PowerPoint presentation) that articulates the value of a specific business project or investment. It presents the rationale for the project, including the benefits, costs, risks, and impact. The main objective is to persuade internal stakeholders to endorse the project.
A business case answers the questions:
- Why should we do this?
- What is the best solution?
- What will happen if we proceed with this investment decision?
Business cases can serve many purposes, but here are a few common reasons for developing one:
- Implementation of a new IT system
- Launching a new product line
- Construction of a new manufacturing plant or data center
- Opening new retail locations or expanding into international markets
- Implementation of new compliance and risk management systems
- Acquiring a competitor or a complementary business
- Investing in building a new capability
- Obtaining additional resources for an ongoing initiative
- Deciding whether to outsource a function
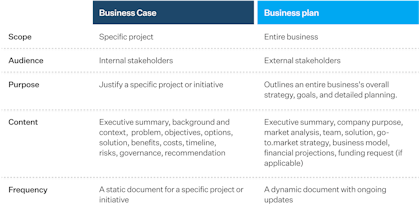
Simply put, a business case justifies a specific project or initiative, while a business plan outlines an entire business's overall strategy, goals, and detailed planning.
Investors use a business plan to make informed decisions about investing. It details the financial, strategic, and operational aspects of a business, helping investors assess the potential return on investment. In contrast, a business case is narrowly focused on a particular project or initiative. It helps stakeholders evaluate the potential impact of that specific project on the business. Both documents require thorough research, careful writing, and effective presentation. Here's an overview of their differences:
Before writing your business case
The fate of your project or initiative will usually lie with a small group of decision makers. The best way to increase your chances of getting a green light is to engage with stakeholders, gather their insights, and build support before writing the business case. Use their input to construct a rough draft and present this draft back to key stakeholders for feedback and approval. Only once you have understood their priorities and concerns should you proceed with writing the final business case.
To get buy-in from your stakeholders, you must tell your "story" so that it is easy to understand the need, the solution you're proposing, and the benefits to the company. Generally, decision-makers will care most about ROI and how your project aligns with the organization's strategic goals – so keep those issues front and center.
In our experience, the business case structure below is the most logical and effective, but you should generally use whatever format or template your company uses. If no templates exist, use the structure below and find a solid template (you'll find a link to a template later in this post).
Whatever structure or template you apply, remember that your story needs to be clear above all else.
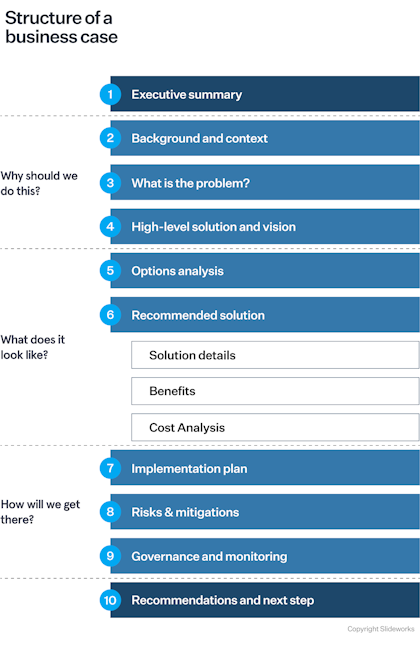
Let's go through each of the 10 sections one-by-one:
1. Executive Summary
A one-page summary providing a concise overview of the business case.
Highlight the key points, including the problem or opportunity, proposed solution, and expected benefits.
We recommend structuring your summary using the Situation-Complication-Solution framework (See How to Write an Effective Executive Summary ) . The executive summary should be the final thing you write.
2. Background and context
Start with the why. Outline the situation and the business problem or opportunity your business case addresses. Clearly describe the problem's impact on the organization.
This section may include an overview of the macro environment and dynamics, key trends driving change, and potential threats or opportunities. Share data that conveys urgency . For example: Is customer satisfaction dropping because of a lack of product features? Is an outdated IT system causing delays in the sales process? Are you seeing growing competition from digital-first players in the market? Are you seeing an opportunity as a result of changing customer needs?
3. What is the problem?
This is a key part of your business case. Your business case is built from your analysis of the problem. If your stakeholders don't understand and agree with your articulation of the problem, they'll take issue with everything else in your business case.
Describe the underlying issues and their solutions using data. You might include customer data, input from end users, or other information from those most affected by the problem.
4. High-level solution and vision
Start with a high-level description of the solution. Clarify the specific, measurable objectives that the project aims to achieve. Ensure these objectives align with the organization's strategic goals.
5. Option analysis
You have now answered the question: Why should we do this project? - and you have outlined a compelling solution.
In this section, you identify and evaluate different options for addressing the problem. Include a "do nothing" option as a baseline for comparison. Assess the pros and cons of each option, considering factors like cost, feasibility, risk, and potential benefits.
See a more in-depth article on how to think about and present risks in our blog post " Mastering Risk Mitigation Slides: A Best Practice Guide with Examples ".
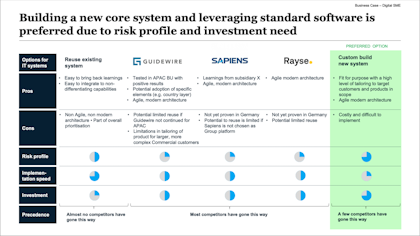
Slide summarizing various options for a new IT system. Example from Slideworks Business Case Template Slide
6. Recommended Solution
Solution Details Propose the preferred solution based on the options analysis. Describe the solution in detail, including scope, deliverables, and key components. Justify why this solution is the best choice.
Benefits Describe the benefits (e.g., cost savings, increased revenue, improved efficiency, competitive advantage). Include both tangible and intangible benefits, but focus on benefits you can quantify. Your stakeholders will want to know the financial impact.
Be very clear about where your numbers come from. Did you get them from colleagues in Marketing, Finance, HR, or Engineering? Stakeholders care about the sources for these assumptions and are more likely to trust your numbers if they come from (or are validated by) people they trust.
Cost Analysis In this section, you provide a detailed breakdown of the costs associated with the proposed solution. Include initial investment, ongoing operational costs, and any potential financial risks.
Compare the costs against the expected benefits to demonstrate return on investment (ROI).
7. Implementation plan
Outline a high-level plan for implementing the proposed solution . Include key milestones, timelines, and dependencies. Describe the resources required, including personnel, technology, and funding.
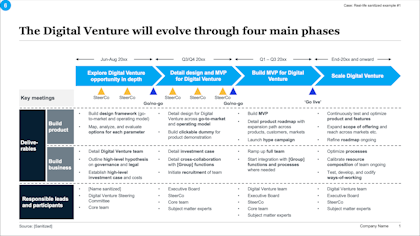
Roadmap example - New digital venture. Slideworks Business Case Template
8. Risks and mitigations
In this section, you highlight potential risks and uncertainties associated with the project. Try to focus on the most important risks (you don't need to account for every potential scenario). These typically include those affecting cost, benefits, and schedule, but they can also include risks to the team, technology, scope, and performance.
Be realistic when you write this section. Transparency will gain the confidence of stakeholders and will demonstrate your foresight and capability.
Consider ranking your identified risk areas according to "likelihood of risk" and "impact of risk" (as shown in the example below). Then, propose mitigation strategies to manage and minimize risks.

Example of Risks Slide - Slideworks Business Case Template

Risks and mitigation slide - Slideworks Business Case Template
9. Governance and monitoring
Establishing a clear governance structure ensures that there is a defined hierarchy of authority, responsibilities, and accountability. A definition of the following groups and roles are often included:
- Steering Committee : A group of senior executives or stakeholders who provide overall strategic direction, make high-level decisions, and ensure that the project aligns with organizational goals.
- Project Sponsor : An individual or group with the authority to provide resources, make critical decisions, and support the project at the highest level. The sponsor is often a senior executive.
- Project Manager : The person responsible for day-to-day management of the project, ensuring that the project stays on track, within budget, and meets its objectives. The project manager reports to the steering committee and project sponsor.
- Project Team : A group of individuals with various skills and expertise necessary to carry out project tasks. The team may include internal staff and external consultants.
You might also define what monitoring and reporting mechanisms that will be used to track the project's progress, identify issues early, and ensure accountability. These mechanisms often include specific Project Management Tools, ongoing status reports, and meetings.
10. Recommendations and next steps
In this last section, you summarize the key points of the business case and make a final recommendation to the decision-makers . Remember to Include your ROI number(s) again and repeat how your project aligns with the organization's strategic goals.
Consider ending your business case with a final slide outlining the immediate actions required to move forward with the recommended solution.
Learn about how to fit in a business case in your commercial due diligence report in our article here .
Business Case PowerPoint template
An effective business case requires both the right content and structure. A strong template and a few best practice examples can ensure the right structure and speed up the process of designing individual slides.
The Slideworks Business Case Template for PowerPoint follows the methodology presented in this post and includes 300 PowerPoint slides, 3 Excel models, and three full-length, real-life case examples created by ex-McKinsey & BCG consultants.
Often, companies have a preferred method of calculating a project's ROI. If this is not the case, you should use the one most appropriate to your project—break-even analysis, payback period, NPV, or IRR.
Key elements of a strong Business Case
Involve subject-matter experts To develop a comprehensive business case, draw on insights from experts who understand the problem's intricacies and potential solutions. Involve colleagues from relevant departments such as R&D, sales, marketing, and finance to ensure all perspectives are considered.
Involve key stakeholders Get input from all relevant team members, including HR, finance, sales, and IT. This collaborative approach ensures the business case is built on verified expert knowledge. Encouraging teamwork and buy-in from internal stakeholders helps build a strong foundation of support.
Understand audience objectives Align your business case with the company’s strategic objectives and future plans. Clearly demonstrate how the project supports long-term company success. Consider the competition for resources and justify the investment by showing its relevance and importance.
Set a clear vision Communicate the purpose, goals, methods, and people involved in the initiative clearly. Detail what the project aims to solve or achieve and its impact on the organization. This clarity helps stakeholders understand the overall vision and direction of the project.
Be on point Be concise and provide only the necessary information needed for informed decision-making. Base your details on facts collected from team members and experts, avoiding assumptions. This precision ensures your business case is credible and actionable.
Check out our Go-To-Market Strategy post to take the next step on bringing your business idea to life.
What is the difference between a project business case and a project charter?
A project charter and a business case are distinct but complementary documents. The business case is created first and serves to justify the project's initiation by detailing its benefits, costs, risks, and alignment with organizational goals. It is used by decision-makers to approve or reject the project.
Once the project is approved, a project charter is often developed to formally authorize the project, outlining its objectives, scope, key stakeholders, and the project manager's authority. A summary of the business case is often included in the project charter.
How long should a business case be?
A comprehensive business case doesn't have a specific page count but should be detailed enough to clearly communicate the project's benefits, costs, risks, and alignment with organizational goals. For small projects, it may be a few pages; for larger or complex projects, it typically ranges from 10-20 word pages (30-50 slides), excluding appendices. Sources: Harvard Business Press - Developing a Business Case
Download our most popular templates
High-end PowerPoint templates and toolkits created by ex-McKinsey, BCG, and Bain consultants

Create a full business case incl. strategy, roadmap, financials and more.

- Market Analysis
Create a full market analysis report to effectively turn your market research into strategic insights

- Market Entry Analysis
Create a best-practice, well-structured market study for evaluating and comparing multiple markets.
Related articles

Timeline Slides (with McKinsey, BCG and Bain examples)
A timeline slide is a visual representation designed to outline a series of key events, milestones, or project phases chronologically.
Dec 23, 2024

Management consulting fees: How McKinsey prices projects
In this article, we’ll explain how consulting projects are priced and the different types of pricing, dive into why firms like McKinsey typically favor fixed fees, explore the range of consulting fees across the industry, and show some real examples of BCG and McKinsey projects and how they were priced.
Dec 7, 2024

The McKinsey problem solving process - A step-by-step guide
At McKinsey, there’s a proven problem solving method that every associate learns from day one — a structured, step-by-step approach that can be applied to almost any business problem.
Nov 20, 2024

- Consulting Toolkit
- Business Strategy
- Consulting Maps Bundle
- Mergers & Acquisitions
- Digital Transformation
- Product Strategy
- Go-To-Market Strategy
- Operational Excellence I
- Operational Excellence II
- Operational Excellence III
- Full Access Bundle
- Consulting PowerPoint Templates
- How it works
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
© 2024 Slideworks. All rights reserved
Denmark : Farvergade 10 4. 1463 Copenhagen K
US : 101 Avenue of the Americas, 9th Floor 10013, New York
The Case HQ

A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing Impactful Business Case Studies
Professor TheCaseHQ
September 11, 2024

Business case studies are powerful tools for demonstrating the value of your products, services, or strategies. They provide real-world examples of how your business has successfully addressed challenges, solved problems, and delivered measurable results for clients or customers. To create a compelling case study that resonates with your target audience, follow this step-by-step guide.
1. Identify the Purpose and Audience
Before you begin writing, clearly define the purpose of your case study and who your target audience is. Are you showcasing a particular service, highlighting a successful project, or demonstrating expertise in a specific industry? Understanding your purpose and audience will guide the tone, content, and structure of your case study, ensuring it speaks directly to those you want to reach.
2. Select a Relevant Case
Choose a case that is both relevant and impactful. The case should exemplify the success of your product or service in addressing a significant challenge. It should also be relatable to your target audience. If possible, select a case that includes measurable outcomes, such as increased revenue, improved efficiency, or enhanced customer satisfaction. Real-world data adds credibility and helps potential clients or customers envision similar success.
3. Conduct Thorough Research
Gather all relevant information about the case, including background details, challenges faced, strategies implemented, and results achieved. Interview key stakeholders involved in the project, such as clients, team members, or partners, to gain insights and firsthand accounts. Collect quantitative data, such as statistics, metrics, and key performance indicators, to support your narrative.
4. Structure Your Case Study
A well-structured case study typically follows a clear and logical flow. Here’s a basic structure to consider:
- Title : A compelling title that highlights the key outcome or benefit.
- Introduction : Briefly introduce the client or company, the challenge they faced, and the solution provided.
- Problem Statement : Describe the specific challenge or problem that needed to be addressed.
- Solution : Detail the approach, strategies, or services used to solve the problem. Highlight any innovative or unique aspects of your solution.
- Results : Present the outcomes, supported by data and evidence. Use charts, graphs, or testimonials to illustrate the impact.
- Conclusion : Summarize the key takeaways and the broader implications of the case study. Include a call to action, inviting readers to learn more or contact you for similar solutions.
5. Focus on the Narrative
While data is crucial, a case study should also tell a story. Use a narrative style to guide readers through the case, from the initial problem to the final solution. Incorporate quotes, anecdotes, and personal insights to make the story more engaging and relatable. A well-told story can help readers connect with the case study on an emotional level, making it more memorable and persuasive.
6. Use Visuals to Enhance Understanding
Visual elements such as charts, graphs, images, and infographics can help clarify complex information and make your case study more visually appealing. Use visuals to break up text and highlight key data points, making it easier for readers to grasp the impact of your work.
7. Review and Edit
After drafting your case study, review it for clarity, coherence, and accuracy. Ensure that the information is presented logically and that the narrative flows smoothly. Check for grammatical errors, typos, and inconsistencies. It’s also helpful to have a colleague or peer review the case study to provide feedback and ensure that it resonates with the intended audience.
Writing an impactful business case study requires careful planning, thorough research, and a clear narrative. By following this step-by-step guide, you can create compelling case studies that effectively showcase your business’s successes and demonstrate the value you bring to your clients or customers. Remember to use data, tell a story, and incorporate visuals to engage your audience and make your case study stand out.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Recent Posts
Comparative Case Studies: Analyzing Success Across Different Industries September 17, 2024
Crafting Case Studies for Marketing: Engaging Your Audience September 16, 2024
How to Write Case Studies that Highlight Problem-Solving Skills September 15, 2024

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
5 Steps for Writing a Case Study for Business (+Templates)
Get professional tips for writing a case study that drives business impact. Learn the best format and research method to use alongside examples & templates.
5 minute read

helped business professionals at:

SHORT ANSWER
What are the 5 steps to write a case study.
- Open with an introductory overview
- Explain the problem in question
- Detail the solutions that solved the problem
- Refer to key results
- Finish with recommendations and next steps
Keep reading for a full breakdown ⤵
What is a case study?
In business, a case study , or customer success story, is a marketing tool that showcases how your product or service helped clients overcome business challenges. It uses statistics, quotes, and specific examples to convincingly highlight your ability to produce results.
What is the purpose of a case study?
The purpose of a case study, usually, is to provide your prospective clients with specific examples of how your products or services can help solve business problems they might be facing.
Case studies legitimize your business activities allowing you to go beyond explaining what you do and focus on how well you do it.
And, in case you were wondering just HOW important case studies are, here’s an item of data to ponder: according to a DemandGen report , 78% of B2B buyers want to review case studies before making a purchase decision.
Another study by Uplift found that at the end of 2023, for the third year in a row, marketers ranked case studies the #1 most effective marketing tactic to increase sales—ahead of general website content, SEO, blog posts, social media, paid ads and other tactics.
How to write a case study?
In business, everyone claims to be the next big thing, but a case study is how you prove it. It shows the real value of your product or service and backs up your claims with real results.
A well-written case study builds trust by showing you can deliver on what you promise and proving the impact your actions have on the bottom line. Here's how to write a case study that engages readers and makes them excited to work with you.
NOTE: If you don't want a slide-by-slide breakdown and just want to see real decks, check out the best case study presentation examples .
Effective case study outline
Introductory overview
The problem or challenge
The solution
Key results
Recommendations and next steps
1. Open with an introductory overview
People don’t usually read case studies. At least not immediately. First, they skim the contents to see if the subject is relevant enough.
How to make sure your case study sticks? At the beginning, place an introductory overview (also called an “executive summary”).
Provide an overview of the whole case. It’s not supposed to be a catchy intro but a full synopsis, detailing the problem at hand, your assumptions, the solutions implemented, and the results achieved.
How to write a case study introduction?
Introduce the company: Start by giving a brief overview of the company that’s the focus of the case study. Share who they are, what they do, and any relevant background.
Introduce the purpose of the case study —specify exactly what you were aiming to achieve.
Define the problem or the most significant challenge. For instance, low conversion rates, a technological issue or high costs. (It could also be a combination of such factors!)
Explain briefly what the solution to the problem was.
Share the most important results your actions produced. Don’t go into too much detail, a few key points will do. It’s best if you can quantify the results: numbers pop!
Keep it short. Usually, 2–4 paragraphs + a few bullet points with key results will do. Consider using an AI rewriter to help you break down complex sentences into clear and concise sentences that effectively convey your message.

While, as its name implies, this section comes at the beginning of your case study, write it last. First, craft the rest of your document, then pick the most important bits and compile them into the introductory overview.
2. Explain the problem in question
In the problem section of your case study, you want to put your reader in the shoes of your client, so that, later on, you can present your company as the miraculous savior.
Paint a clear picture of the challenge your product or service solves, and focus on how difficult the situation was for the client before your solution came along.
The goal is to create a sense of urgency and connection—making it easy for readers to relate and feel the weight of the problem. This emotional engagement is key to highlighting just how valuable your solution is.
How to write a “problem” section in a case study?
In a single sentence, describe your customer’s business challenges and objectives.
Explain the problem your customer faced that prevented them from achieving those objectives prior to working with you.
If that was the case, mention other solutions your client experimented with that didn’t work out and explain why.
Make it clear how the issue or problem impacted the client’s business results so that it’s easy to understand why a solution was badly needed.

3. Detail the solutions implemented to solve the problem
Here comes the moment to toot your own horn a bit (and also that moment when you can get slightly technical).
Present your solutions in reference to the issue your client was dealing with and make it obvious that those are easily replicable for all future cases. Of course, the exact formula for this section will depend on your industry and mode of operation.
Sometimes a 2–3 paragraph summary will be enough. In other cases, you’ll need to include more detailed technical specs regarding the solution you implemented.
How to write a "solution" section in a case study?
Focus on your customer’s experience in using your product or services.
Explain the process : say how long it took to get the solution up and running and what teams on your customer’s end were involved.
Highlight the features of your product or service that turned out to be the most beneficial to your customer.
If possible, attach or link to relevant assets that will work as real-life examples of your solution (unless, of course, the information is highly sensitive).
Always run your case study by your client’s marketing team before you go live. Even if you’re using direct quotes or verifiable results, it’s ultimately their decision whether or not to make certain information freely available.

4. Refer to key results
In business, nothing speaks louder than ROI and you know it.
Prospective customers reading your case study won’t be bothered to take notice of your state-of-the-art technology or innovative approach. Neither will they care about your past customers’ happiness. What they want to know is this: Will that help me save or make money? When writing a case study, your job is to present results in a way that answers the above question with a resounding YES.
Here’s how to write about results:
In a few bullet points, list numerical results your solution delivered to the client.
Ideally, you’ll want to include revenue-related data: increase in clients’ base, more demos booked, higher conversion rates, or optimized pricing.
If you can’t (or aren’t allowed to) share hard sales numbers, refer to softer KPIs: time saved, customer happiness scores, expanding the community, or enhancing brand visibility.
Make it blatantly obvious that such results are easily replicable.

If possible, by all means include quotes from your client. Results should speak for themselves, obviously, but showing the real human whose problems you solved makes for a much more powerful narrative. Plus, it further adds credibility to the case study. Start by preparing a list of powerful case study questions to guide your client interviews.
5. Finish with recommendations and next steps
Everyone enjoys a solid epilogue. To end on a high note, include a list of key findings from your case study.
Even if a given reader won’t decide to get in touch with you, at least you’ll provide them with a valuable source of knowledge—sometimes that’s enough to keep your company top of mind in the future. Now, not every case study requires a call to action (especially if your main purpose is to inform and educate rather than convert, which is okay, too), but for those more commercially-oriented ones, do add it. Make your CTA singular and clear —if the most desired action is to reach out to you, leave your contact details, if you’d rather direct prospects to a landing page or a welcome screen, add a button.
For your reference, here’s an example of our very own case study, showing how, at Storydoc, we helped the Spot company boost some of their key metrics: Learn How Spot by NetApp boosted their conversion rates 2x .
Interactive case study templates
No matter how great the contents of your case study might be, if you fail to present it in an eye-pleasing way, most likely, no one will really read it.
Interactive case study templates help bring your story to life with features like data visualization, clickable elements, and the option to add links or multimedia.
This makes it easier for your audience to follow along and understand your message and helps you stand out from the competition.
Just grab one.
Tips on preparing a case study
Before writing a case study, it’s important to take the time to prepare properly. It’s more than just sharing a success story—you want to gather the right details and present them in a way that really connects with your audience.
By doing this groundwork, you can ensure your case study demonstrates your value but also builds a sense of credibility and trust that sticks with potential clients.
Case study preparation tips:
Determine a customer use case
Go over existing clients
Reach out to the happy clients
Set success criteria
Set measurements
Set time period for observation
Conduct post interview to assess results
Get data from client
Get client approval
For more information, check out our guide on how to create a case study .

Hi, I'm John, Editor-in-chief at Storydoc. As a content marketer and digital writer specializing in B2B SaaS, my main goal is to provide you with up-to-date tips for effective business storytelling and equip you with all the right tools to enable your sales efforts.
Found this post useful?
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Get notified as more awesome content goes live
(No spam, no ads, opt-out whenever)
You've just joined an elite group of people that make the top performing 1% of sales and marketing collateral.

Make your best case study to date.
Try Storydoc for free for 14 days (keep anything you make for ever!)

How to Write a Case Study: The Compelling Step-by-Step Guide

Is there a poignant pain point that needs to be addressed in your company or industry? Do you have a possible solution but want to test your theory? Why not turn this drive into a transformative learning experience and an opportunity to produce a high-quality business case study? However, before that occurs, you may wonder how to write a case study.
You may also be thinking about why you should produce one at all. Did you know that case studies are impactful and the fifth most used type of content in marketing , despite being more resource-intensive to produce?
Below, we’ll delve into what a case study is, its benefits, and how to approach business case study writing:
Definition of a Written case study and its Purpose
A case study is a research method that involves a detailed and comprehensive examination of a specific real-life situation. It’s often used in various fields, including business, education, economics, and sociology, to understand a complex issue better.
It typically includes an in-depth analysis of the subject and an examination of its context and background information, incorporating data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and existing literature.
The ultimate aim is to provide a rich and detailed account of a situation to identify patterns and relationships, generate new insights and understanding, illustrate theories, or test hypotheses.
Importance of Business Case Study Writing
As such an in-depth exploration into a subject with potentially far-reaching consequences, a case study has benefits to offer various stakeholders in the organisation leading it.
- Business Founders: Use business case study writing to highlight real-life examples of companies or individuals who have benefited from their products or services, providing potential customers with a tangible demonstration of the value their business can bring. It can be effective for attracting new clients or investors by showcasing thought leadership and building trust and credibility.
- Marketers through case studies and encourage them to take action: Marketers use a case studies writer to showcase the success of a particular product, service, or marketing campaign. They can use persuasive storytelling to engage the reader, whether it’s consumers, clients, or potential partners.
- Researchers: They allow researchers to gain insight into real-world scenarios, explore a variety of perspectives, and develop a nuanced understanding of the factors that contribute to success or failure. Additionally, case studies provide practical business recommendations and help build a body of knowledge in a particular field.
How to Write a Case Study – The Key Elements

Considering how to write a case study can seem overwhelming at first. However, looking at it in terms of its constituent parts will help you to get started, focus on the key issue(s), and execute it efficiently and effectively.
Problem or Challenge Statement
A problem statement concisely describes a specific issue or problem that a written case study aims to address. It sets the stage for the rest of the case study and provides context for the reader.
Here are some steps to help you write a case study problem statement:
- Identify the problem or issue that the case study will focus on.
- Research the problem to better understand its context, causes, and effects.
- Define the problem clearly and concisely. Be specific and avoid generalisations.
- State the significance of the problem: Explain why the issue is worth solving. Consider the impact it has on the individual, organisation, or industry.
- Provide background information that will help the reader understand the context of the problem.
- Keep it concise: A problem statement should be brief and to the point. Avoid going into too much detail – leave this for the body of the case study!
Here is an example of a problem statement for a case study:
“ The XYZ Company is facing a problem with declining sales and increasing customer complaints. Despite improving the customer experience, the company has yet to reverse the trend . This case study will examine the causes of the problem and propose solutions to improve sales and customer satisfaction. “
Solutions and interventions

Business case study writing provides a solution or intervention that identifies the best course of action to address the problem or issue described in the problem statement.
Here are some steps to help you write a case study solution or intervention:
- Identify the objective , which should be directly related to the problem statement.
- Analyse the data, which could include data from interviews, observations, and existing literature.
- Evaluate alternatives that have been proposed or implemented in similar situations, considering their strengths, weaknesses, and impact.
- Choose the best solution based on the objective and data analysis. Remember to consider factors such as feasibility, cost, and potential impact.
- Justify the solution by explaining how it addresses the problem and why it’s the best solution with supportive evidence.
- Provide a detailed, step-by-step plan of action that considers the resources required, timeline, and expected outcomes.
Example of a solution or intervention for a case study:
“ To address the problem of declining sales and increasing customer complaints at the XYZ Company, we propose a comprehensive customer experience improvement program. “
“ This program will involve the following steps:
- Conducting customer surveys to gather feedback and identify areas for improvement
- Implementing training programs for employees to improve customer service skills
- Revising the company’s product offerings to meet customer needs better
- Implementing a customer loyalty program to encourage repeat business “
“ These steps will improve customer satisfaction and increase sales. We expect a 10% increase in sales within the first year of implementation, based on similar programs implemented by other companies in the industry. “
Possible Results and outcomes

Writing case study results and outcomes involves presenting the impact of the proposed solution or intervention.
Here are some steps to help you write case study results and outcomes:
- Evaluate the solution by measuring its effectiveness in addressing the problem statement. That could involve collecting data, conducting surveys, or monitoring key performance indicators.
- Present the results clearly and concisely, using graphs, charts, and tables to represent the data where applicable visually. Be sure to include both quantitative and qualitative results.
- Compare the results to the expectations set in the solution or intervention section. Explain any discrepancies and why they occurred.
- Discuss the outcomes and impact of the solution, considering the benefits and drawbacks and what lessons can be learned.
- Provide recommendations for future action based on the results. For example, what changes should be made to improve the solution, or what additional steps should be taken?
Example of results and outcomes for a case study:
“ The customer experience improvement program implemented at the XYZ Company was successful. We found significant improvement in employee health and productivity. The program, which included on-site exercise classes and healthy food options, led to a 25% decrease in employee absenteeism and a 15% increase in productivity . “
“ Employee satisfaction with the program was high, with 90% reporting an improved work-life balance. Despite initial costs, the program proved to be cost-effective in the long run, with decreased healthcare costs and increased employee retention. The company plans to continue the program and explore expanding it to other offices .”
Case Study Key takeaways

Key takeaways are the most important and relevant insights and lessons that can be drawn from a case study. Key takeaways can help readers understand the most significant outcomes and impacts of the solution or intervention.
Here are some steps to help you write case study key takeaways:
- Summarise the problem that was addressed and the solution that was proposed.
- Highlight the most significant results from the case study.
- Identify the key insights and lessons , including what makes the case study unique and relevant to others.
- Consider the broader implications of the outcomes for the industry or field.
- Present the key takeaways clearly and concisely , using bullet points or a list format to make the information easy to understand.
Example of key takeaways for a case study:
- The customer experience improvement program at XYZ Company successfully increased customer satisfaction and sales.
- Employee training and product development were critical components of the program’s success.
- The program resulted in a 20% increase in repeat business, demonstrating the value of a customer loyalty program.
- Despite some initial challenges, the program proved cost-effective in the long run.
- The case study results demonstrate the importance of investing in customer experience to improve business outcomes.
Steps for a Case Study Writer to Follow

If you still feel lost, the good news is as a case studies writer; there is a blueprint you can follow to complete your work. It may be helpful at first to proceed step-by-step and let your research and analysis guide the process:
- Select a suitable case study subject: Ask yourself what the purpose of the business case study is. Is it to illustrate a specific problem and solution, showcase a success story, or demonstrate best practices in a particular field? Based on this, you can select a suitable subject by researching and evaluating various options.
- Research and gather information: We have already covered this in detail above. However, always ensure all data is relevant, valid, and comes from credible sources. Research is the crux of your written case study, and you can’t compromise on its quality.
- Develop a clear and concise problem statement: Follow the guide above, and don’t rush to finalise it. It will set the tone and lay the foundation for the entire study.
- Detail the solution or intervention: Follow the steps above to detail your proposed solution or intervention.
- Present the results and outcomes: Remember that a case study is an unbiased test of how effectively a particular solution addresses an issue. Not all case studies are meant to end in a resounding success. You can often learn more from a loss than a win.
- Include key takeaways and conclusions: Follow the steps above to detail your proposed business case study solution or intervention.
Tips for How to Write a Case Study
Here are some bonus tips for how to write a case study. These tips will help improve the quality of your work and the impact it will have on readers:
- Use a storytelling format: Just because a case study is research-based doesn’t mean it has to be boring and detached. Telling a story will engage readers and help them better identify with the problem statement and see the value in the outcomes. Framing it as a narrative in a real-world context will make it more relatable and memorable.
- Include quotes and testimonials from stakeholders: This will add credibility and depth to your written case study. It also helps improve engagement and will give your written work an emotional impact.
- Use visuals and graphics to support your narrative: Humans are better at processing visually presented data than endless walls of black-on-white text. Visual aids will make it easier to grasp key concepts and make your case study more engaging and enjoyable. It breaks up the text and allows readers to identify key findings and highlights quickly.
- Edit and revise your case study for clarity and impact: As a long and involved project, it can be easy to lose your narrative while in the midst of it. Multiple rounds of editing are vital to ensure your narrative holds, that your message gets across, and that your spelling and grammar are correct, of course!
Our Final Thoughts
A written case study can be a powerful tool in your writing arsenal. It’s a great way to showcase your knowledge in a particular business vertical, industry, or situation. Not only is it an effective way to build authority and engage an audience, but also to explore an important problem and the possible solutions to it. It’s a win-win, even if the proposed solution doesn’t have the outcome you expect. So now that you know more about how to write a case study, try it or talk to us for further guidance.
Are you ready to write your own case study?
Begin by bookmarking this article, so you can come back to it. And for more writing advice and support, read our resource guides and blog content . If you are unsure, please reach out with questions, and we will provide the answers or assistance you need.
Categorised in: Resources
This post was written by Premier Prose
© 2025 Copyright Premier Prose. Website Designed by Ubie

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
- Cookie Policy
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
More information about our Cookie Policy
Stay ahead of the AI revolution.

How to Write a Case Study for Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
In the world of business, case studies are one of the most powerful tools for showcasing success stories, demonstrating problem-solving skills, and building credibility and trust. Case studies allow potential clients to see the real-world impact of your services and can help you stand out from your competitors. But creating a compelling case study can be a daunting task, especially if you don't know where to start. In this step-by-step guide, we'll show you everything you need to know to write a successful business case study.
Understanding the Purpose of a Business Case Study
The purpose of a business case study is to highlight the value of your services to potential clients by showcasing your success stories and problem-solving skills. By presenting a clear, relevant, and compelling story, you can build trust and credibility with potential clients and demonstrate your ability to deliver measurable results.
However, creating a business case study requires more than just presenting a success story. You need to provide context and detail to help potential clients understand the challenges you faced and the solutions you implemented. This additional information can help potential clients see how your services can benefit their own businesses.
Showcasing Success Stories
One of the key benefits of a business case study is that it allows you to showcase your success stories. By highlighting your past successes, you can demonstrate your expertise in your field and build trust and credibility with potential clients. When selecting a success story, choose one that showcases your ability to deliver measurable results and has a strong emotional impact on the reader.
For example, if you are a marketing agency, you could showcase a case study where you helped a small business increase their website traffic by 200% in just three months. By providing details on the strategies you used, such as search engine optimization and social media marketing, potential clients can see the specific ways your services can benefit their own businesses.
Demonstrating Problem-Solving Skills
Another key benefit of a business case study is that it allows you to demonstrate your problem-solving skills. By presenting a clear and compelling solution to a relevant business problem, you can position yourself as an expert in your field and build trust and credibility with potential clients.
For instance, if you are a software development company, you could showcase a case study where you helped a client solve a complex software integration issue. By providing details on the specific challenges you faced and the steps you took to solve the problem, potential clients can see how your problem-solving skills can benefit their own businesses.
Building Credibility and Trust
Finally, a business case study can help you build credibility and trust with potential clients. By presenting your success stories and problem-solving skills in a clear and compelling way, you can demonstrate your ability to deliver results and build trust with your potential clients.
However, it's important to remember that a business case study is just one tool in your marketing arsenal. You should also consider other ways to build credibility and trust, such as providing testimonials from satisfied clients and showcasing your industry awards and certifications.
Overall, a well-crafted business case study can be a powerful tool for demonstrating your value to potential clients. By providing context and detail, showcasing your success stories, and demonstrating your problem-solving skills, you can build trust and credibility with potential clients and position yourself as an expert in your field.
Identifying the Right Subject for Your Case Study
The first step in writing a business case study is to identify the right subject for your case study. Here are a few things to keep in mind when selecting a subject:
Selecting a Relevant Business Problem
The first thing to consider when selecting a subject for your case study is to choose a relevant business problem. Your case study should highlight your ability to solve a real-world problem that is relevant to your potential clients. Look for problems that your clients are likely to face in their day-to-day operations.
Choosing a Compelling Client Story
The second thing to consider is to select a client story that is compelling and emotionally engaging. Choose a story that has a strong human interest component and that resonates with your potential clients. This will help you connect with your readers on an emotional level and make your case study more effective.
Ensuring Measurable Results
The final thing to consider is to ensure that your case study showcases measurable results. Your case study should demonstrate how your services helped your client achieve quantifiable and significant results, such as increased revenue, improved efficiency, or higher customer satisfaction.
Conducting Thorough Research
The next step in writing a successful business case study is to conduct thorough research. Here are a few tips to help you conduct effective research:
Reviewing Company Documents
Start by reviewing relevant company documents, such as annual reports, financial statements, and marketing materials. This will give you a better understanding of your client's business and the challenges they face.
Interviewing Key Stakeholders
The next step is to interview key stakeholders, such as your client's senior management team, department heads, and employees. This will help you gain insight into your client's business and the challenges they face.
Analyzing Competitor Case Studies
Finally, analyze case studies of your client's competitors to gain a better understanding of the industry and the challenges faced by your client.
Structuring Your Business Case Study
The final step in writing a successful business case study is to structure your case study effectively. Here are the key elements of an effective case study:
Introduction and Background
Start with an introduction that provides background information on your client and their business. This should include a brief overview of the industry and the challenges faced by your client.
Problem Statement and Challenges
The next section should clearly state the problem faced by your client and the challenges they faced in addressing the problem. This should be presented in a clear and concise manner.
Solution Implementation
The next section should detail the solution you developed to address the problem faced by your client. This should include the steps taken to implement the solution and any challenges faced along the way.
Results and Impact
The next section should provide an overview of the measurable results achieved by your client as a result of your solution. This should include details on revenue growth, cost savings, or other significant improvements.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Finally, conclude your case study with a summary of the key takeaways and lessons learned. This should include a brief overview of the impact of your solution and the benefits of working with your company.
By following these steps, you can create a compelling and effective business case study that showcases your success stories, problem-solving skills, and ability to deliver measurable results. Remember to keep your writing clear, concise, and engaging, and use visuals and formatting to break up large blocks of text and keep your readers engaged.
ChatGPT Prompt for Writing a Case Study for Business
Chatgpt prompt.
Please compose a thorough and detailed analysis of a specific business situation, including relevant background information, key players and stakeholders, challenges faced, strategies employed, and outcomes achieved. Your case study should provide a comprehensive understanding of the business issue at hand and offer insights and recommendations for future decision-making.
[ADD ADDITIONAL CONTEXT. CAN USE BULLET POINTS.]
Recommended Articles
How to write a theme: a step-by-step guide, how to write a research title: a step-by-step guide, feeling behind on ai, get the latest ai.

Get Your Free ChatGPT Training!

ChatGPT: Zero to Power User Cheat Sheet
- Top AI tools to use at work.
- Prompt frameworks.
- What NOT to use ChatGPT for.
.jpg)
Free AI Course for Professionals

Why 400,000+ Professionals Use The Neuron to Have An Edge Over Peers At Work
.jpg)

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Feb 26, 2020 · Three expert HBS case writers share their insights on how to write a great business case study that will inspire passionate classroom discussion and transmit key educational concepts.
Sep 24, 2024 · Below, we illustrate the steps to writing one that will sway them. The need for a business case is that it collects the financial appraisal, proposal, strategy and marketing plan in one document and offers a full look at how the project will benefit the organization.
Mar 30, 2023 · A business case study is an in-depth look at a specific company or organization that examines how a business solved a problem, achieved success, or faced failure. Case studies are often used by businesses to demonstrate the effectiveness of their strategies and solutions.
Jun 11, 2024 · This guide, written by former consultants from McKinsey and Bain, will help you write a compelling business case. It provides the steps and best practices to secure the necessary support and resources for a successful project.
May 14, 2024 · Learn how to write a case study that showcases your success. Use our template and proven techniques to create a compelling case study for your clients.
Sep 11, 2024 · Writing an impactful business case study requires careful planning, thorough research, and a clear narrative. By following this step-by-step guide, you can create compelling case studies that effectively showcase your business’s successes and demonstrate the value you bring to your clients or customers.
Get professional tips for writing a case study that drives business impact. Learn the best format and research method to use alongside examples & templates.
Feb 11, 2023 · Here are some steps to help you write a case study problem statement: Identify the problem or issue that the case study will focus on. Research the problem to better understand its context, causes, and effects. Define the problem clearly and concisely. Be specific and avoid generalisations.
Jun 13, 2024 · Writing effective business case studies is something that will take some time and practice on your part. Still, there are some tips and best practices you can follow to write better case studies today. First, understand the importance of selecting the right client to highlight for your case study.
Learn how to write an effective case study for your business with our step-by-step guide. Includes ChatGPT prompt. In the world of business, case studies are one of the most powerful tools for showcasing success stories, demonstrating problem-solving skills, and building credibility and trust.